Biggest ransomware threat is encryption of shared cloud files

The cybercriminal's most effective weapon in a ransomware attack is the network itself, which enables the malicious encryption of shared files on network servers, especially files stored in infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) cloud providers.
This is according to a new report from threat detection specialist Vectra which finds that by encrypting files that are accessed by many business applications across the network, attackers achieve an economy of scale faster and far more damaging than encrypting files on individual devices.
"The fallout from ransomware attacks against cloud service providers is far more devastating when the business systems of every cloud-hosted customer are encrypted," says Chris Morales, head of security analytics at Vectra. "Today's targeted ransomware attacks are an efficient, premeditated criminal threat with a rapid close and no middleman."
The report also looks at the prevalence of network file encryption attacks by industry and by region. Finance and insurance is the most attacked industry sector, while California is the most attacked region of the US. In Europe most attacks of this type are seen in Germany, followed by Switzerland.
You can get the full report from the Vectra site and there's an infographic summary of the findings below.
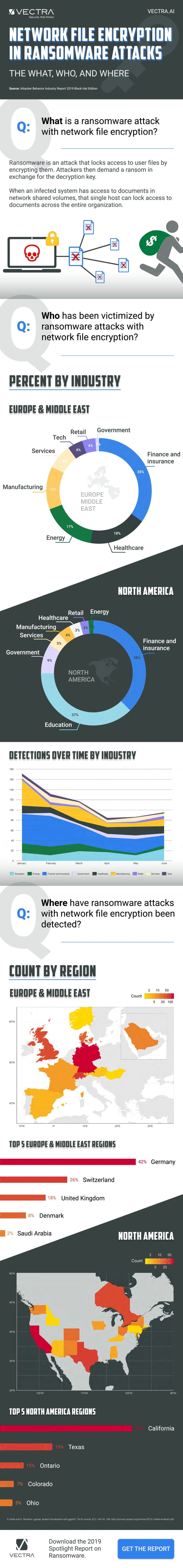
Photo Credit: LeoWolfert/Shutterstock
