AI-powered malware surges as cybercriminals exploit automation and geopolitical tensions

Trellix has published its latest CyberThreat Report: October 2025, highlighting a clear rise in the use of AI-powered tools and malware by cybercriminals.
Drawing on global threat intelligence gathered between April and September 2025, the report explores how automation, geopolitics, and AI are reshaping modern attack methods.
Ransomware remains one of the most disruptive forms of cybercrime, with industrial operations now the most heavily targeted sector. Attackers appear to recognize that disrupting production and logistics increases the pressure on victims to pay.
The report also details the rapid emergence of new ransomware players and shifting patterns in state-sponsored activity.
“We’re seeing a transformation of threat actor behavior, with two clear and converging trends: automation and geopolitical malice,” John Fokker, VP of Threat Intelligence Strategy at Trellix, said. “As threat actors near the AI adoption inflection point, demonstrating a more structured use of AI-powered attack methods over the last six months, they’ll be able to chain multiple AI-driven attacks with unprecedented fluidity, significantly shortening and diversifying the time required to execute an attack. Consequently, security teams must prioritize a defense-in-depth strategy, focusing on multiple detection opportunities across the entire attack kill-chain.”
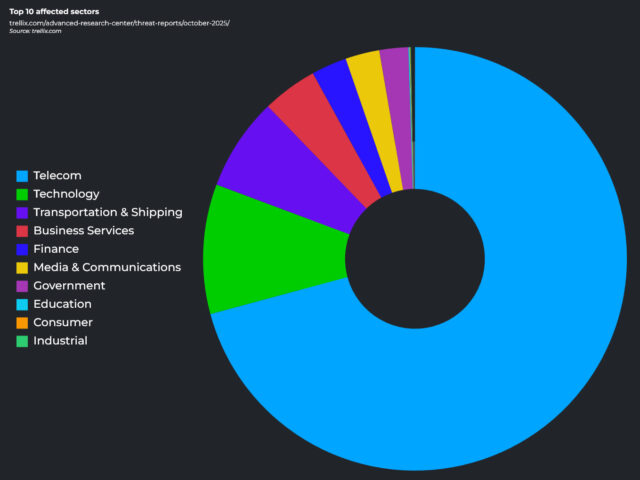
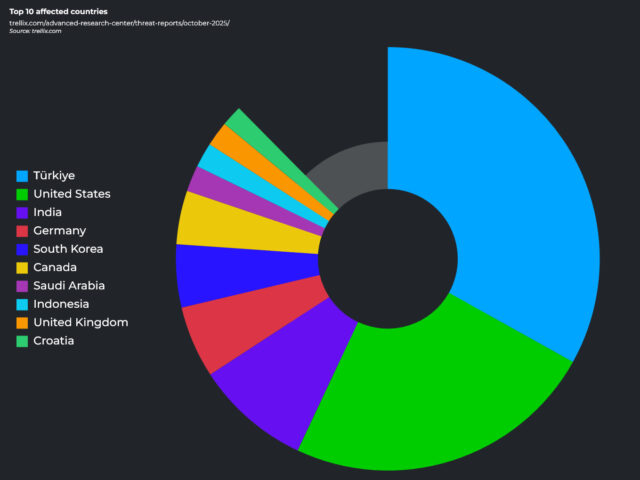
The security firm detected more than half a million advanced persistent threat (APT) incidents across 1,221 unique campaigns in 121 countries and 14 sectors -- a huge escalation in activity. Türkiye and the United States saw the highest number of incidents, while telecommunications was, perhaps unsurprisingly, the most targeted industry.
Trellix also identified a worrying increase in insider threats linked to North Korea, with state-sponsored operatives attempting to infiltrate US organizations by posing as legitimate IT workers. This shift toward “malware-less” espionage marks an evolution in how nation-states pursue access to sensitive systems.
In the criminal underworld, the Russian-speaking ransomware group Qilin has rapidly gained ground following the collapse of RansomHub. Trellix’s data shows Qilin favoring industrial firms for almost a third of its attacks, followed by consumer services and financial companies.
This trend suggests attackers are adjusting their tactics to exploit sectors viewed as being most vulnerable to operational disruption.
AI continues to reshape both attack and defense with Trellix identifying the AI-powered infostealer LameHug and a fully automated, AI-generated ransomware appearing on GitHub.
Organizations are also using AI to enhance their own detection and response however, aided by greater data sharing and real-time intelligence from platforms.
You can view the CyberThreat Report: October 2025 on Trellix’s site here.
What do you think about the rise of AI-powered cyberattacks? Let us know in the comments.
Image credit: BeeBright/depositphotos.com
