
Japanese companies are a prime target for nation-state attacks
A new report from cloud risk and detection specialist Rapid7 reveals that Japanese businesses have become a significant target for state-sponsored cyberattacks.
This increased vulnerability has been driven by a fragile global economy and increased political and diplomatic tensions. The Japanese automotive industry and financial services sectors are of particular interest to these actors due to their global reach.

Three must-know cybersecurity building blocks
The increasing sophistication of cybercriminals significantly influences the rise in cybercrime, the frequent lack of sufficient cybersecurity measures, and the high profitability of cybercrime. Cybercriminals constantly refine their skills, developing advanced malware and phishing techniques to bypass security protocols. This progress often outpaces many businesses' and individuals' ability to safeguard their digital assets -- as a lack of resources, underestimation of risk, or insufficient awareness often results in inadequate cybersecurity measures. Further fueling this upward trend is the lucrative nature of cybercrime, with offenders able to amass significant profits from stolen money or data, often with a low risk of apprehension due to the anonymity of the internet and digital currencies.
A recent BlackBerry Global Threat Intelligence Report observed up to 12 attacks per minute from December 2022 to February 2023, and the number of unique attacks using new malware samples skyrocketed by 50 percent -- from one per minute in the previous report to 1.5 per minute during this reporting period. The most common weapons were droppers, downloaders, remote access tools (RATs), and ransomware, with the most significant target being the healthcare industry.

Memory-based attacks increase as attackers dodge cloud defenses
A new report shows a 1,400 percent increase in fileless or memory-based attacks, which exploit existing software, applications, and protocols to perform malicious activities against cloud-based systems.
The research from Aqua Security's Nautilus research team collected honeypot data over a six-month period and shows that more than 50 percent of the attacks focused on defense evasion.

Securing supply chains: Navigating risks in the evolving threat landscape
Across the interconnected global economy, complex supply chains ensure the seamless flow of goods and services across every industry. However, as cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations throughout this ecosystem are, often unknowingly, being exposed to more and more security risks as a direct result of being part of the chain. This creates a range of critical challenges for organizations whose very existence is dependent on the reliability and integrity of their supply chains at all their various levels.
Understanding the various stages of contemporary supply chains -- from material sourcing to manufacturing, transportation, warehousing, and distribution -- is essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities, with each stage susceptible to different types of risks.

Hacking and why it can be good for cybersecurity [Q&A]
Hacking tends to have something of a bad name, but there are many hackers who do good work, identifying flaws before they can be exploited in cyberattacks.
However, many of these people operate in the shadows for fear of being prosecuted for violating legislation. We talked to Laurie Mercer, director of sales engineering at security platform HackerOne, to discuss whether ethical hackers need to be more open about their activities in order to bring about change and how ethical hacking is making organizations safer.

'Shadow AI' could lead to a wave of insider threats
Poor data controls and the advent of new generative AI tools based on Large Language Models (LLMs) will lead to a spike in insider data breaches over the coming year, says cybersecurity company Imperva.
As LLM-powered chatbots have become more powerful, many organizations have implemented complete bans or restricted what data can be shared with them. However, since an overwhelming majority (82 percent) have no insider risk management strategy in place, they remain blind to instances of employees using generative AI to help them with tasks.

Construction and transport are most targeted by cybercriminals
The construction sector (with an average of 226 incidents annually) is the most targeted by cyber criminals closely followed by transport (167), wholesale trade (138), manufacturing (116) and retailers (105).
A new report from ReliaQuest, based on data from 35,000 incidents affecting its clients, shows the most detected attack technique is the attempted exploitation of exposed remote services, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) and remote desktop protocol (RDP).
Cybercriminals use AI to make malware less detectable
Cybercriminals are using AI-created malware that is adept at avoiding detection by traditional antivirus models, according to the latest report from Acronis.
The report also finds email attacks and ransomware cases have exploded relative to last year. Acronis-monitored endpoints are picking up valuable data about how cybercriminals operate and how some attacks have become more intelligent, sophisticated, and difficult to detect.

Three of the world's most expensive phishing attacks... and how they could have been prevented
A number of high-profile cyber-attacks in recent years have thrust cybersecurity back into the spotlight. In light of the HAFNIUM hack, cybersecurity has become a major focus for many businesses. Although the hack itself was not the result of human error, it was a wake-up call for organizations to make sure they were fully protected.
The UK's Department for DCMS’ Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2021 revealed that phishing is still the most common cause of cybersecurity breaches, accounting for 83 percent of all successful attacks.

Attackers exploit the growing use of mobile devices
The growth in mobile device and app usage has created a growing attack surface, with 60 percent of global web traffic now coming from mobile devices. So it's not surprising that increasing numbers of cybercriminals and nation state actors want to exploit these areas of vulnerability.
The latest Global Mobile Threat Report from Zimperium finds that 80 percent of phishing sites now either specifically target mobile devices or are built to function on both mobile devices and desktops.
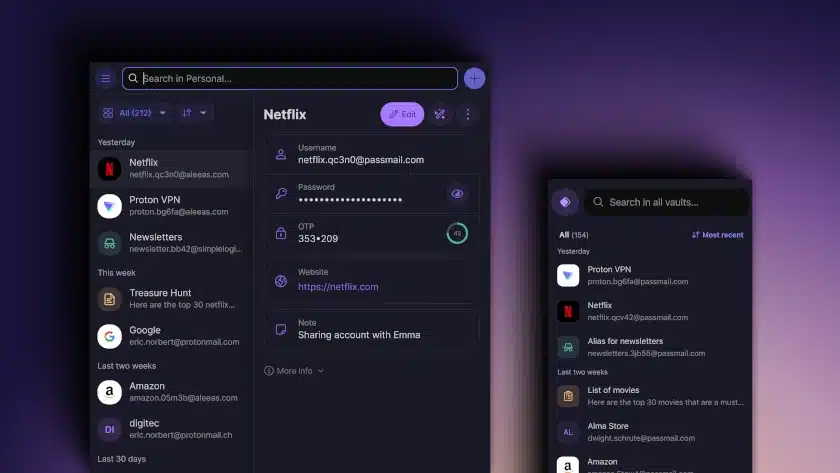
Proton Pass free password manager emerges from beta
Although alternative technologies continue to make inroads, most of us are still heavily reliant on passwords to secure our digital identities.
Proton, the company behind Proton Mail, Proton VPN and other products, launched a new, free password manager called -- you'll have guessed already -- Proton Pass in beta a couple of months ago.

Majority are worried about the safety and accuracy of ChatGPT
As generative AI tools continue to make the news there are growing concerns over safety and security as well as the accuracy of information produced.
Most people don't trust ChatGPT and have worries about its security and safety according to a new survey from Malwarebytes. The research shows that 81 percent are concerned about security and safety risks.

DDoS attacks more than doubled in 2022
New research from Nexusguard shows that last year DDoS attacks worldwide increased by 115.1 percent over the 2021 level.
Attackers have also continued to alter their threat vectors by targeting the application platforms, online databases, and cloud-based storage systems within Internet Service Providers (ISPs). This has resulted in a significantly greater impact globally as organizations continue to move more of their workloads to the cloud.

Enterprise SIEMs miss 76 percent of attack techniques
Security information and event management systems (SIEMs) are missing detections for 76 percent of MITRE ATT&CK techniques that adversaries use to breach their environments, according to a new report.
Produced by CardinalOps, the study analyzes real-world data from production SIEMs -- including Splunk, Microsoft Sentinel, IBM QRadar, and Sumo Logic -- covering more than 4,000 detection rules, nearly one million log sources, and hundreds of unique log source types.

Threat landscape is getting worse say CISOs
A new study of over 200 CISOs and senior security leaders at organizations with over 5,000 employees shows that 93 percent have suffered at least one cyberattack in the last year and all of them think the security landscape is worsening.
The research from Censys also shows that 53 percent identify the need to secure their organization's entire attack surface as their top priority.
