Illicit code signing certificates worth more than passports on the dark web

Code signing certificates are used to verify the authenticity and integrity of software and are a vital element of internet and enterprise security. By taking advantage of compromised code signing certificates, cybercriminals can install malware on enterprise networks and consumer devices.
A study for machine identity protection company Venafi by the Cyber Security Research Institute shows that digital code signing certificates are changing hands on the dark web for up to $1,200, making them worth more than credit cards, counterfeit US passports and even handguns.
"We've known for a number of years that cyber criminals actively seek code signing certificates to distribute malware through computers," says Peter Warren, chairman of the CSRI. "The proof that there is now a significant criminal market for certificates throws our whole authentication system for the internet into doubt and points to an urgent need for the deployment of technology systems to counter the misuse of digital certificates."
Armed with a stolen certificate cyber criminals can do a number of things including launching man-in-the-middle attacks, installing malware, stealing data and spoofing websites. With a 35 percent growth in certificate usage predicted for this year the potential attack surface is growing too.
"Our research proves that code signing certificates are lucrative targets for cyber criminals," adds Kevin Bocek, chief security strategist for Venafi. "With stolen code signing certificates, it's nearly impossible for organizations to detect malicious software. Any cyber criminal can use them to make malware, ransomware, and even kinetic attacks trusted and effective. In addition, code signing certificates can be sold many times over before their value begins to diminish, making them huge money makers for hackers and dark web merchants. All of this is fuelling the demand for stolen code signing certificates."
You can see more of the report's findings in the infographic below.
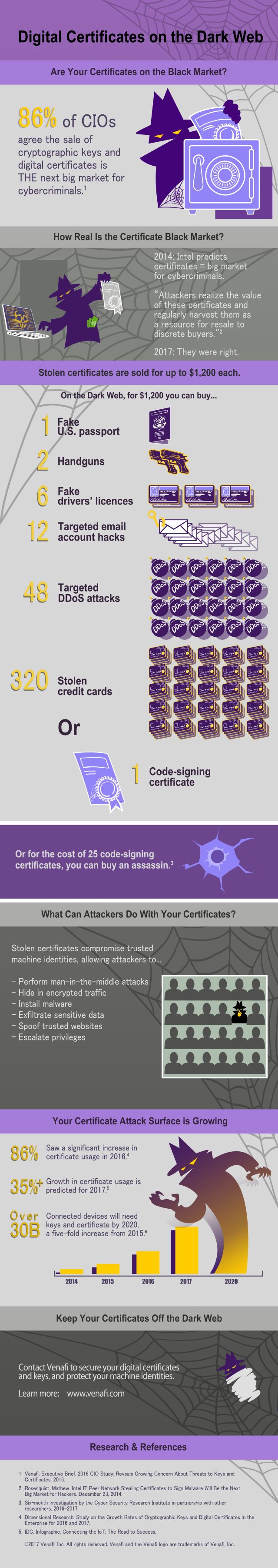
Image Credit: maxkabakov / depositphotos.com