
X starts the rollout of update that renders blocking near-pointless
Back in September, Elon Musk announced upcoming changes to the blocking feature of X. Once fully implemented, the change means that when an X user blocks someone, that blocked user will still be able to see all of the content posted by the blocker, although no interaction will be possible.
The precise reasons for changing the functionality of blocking in this way is not really clear, but it is something that has sparked concern. In addition to risks to privacy, there are also worries about what the changes could mean for victims of cyber-stalking.
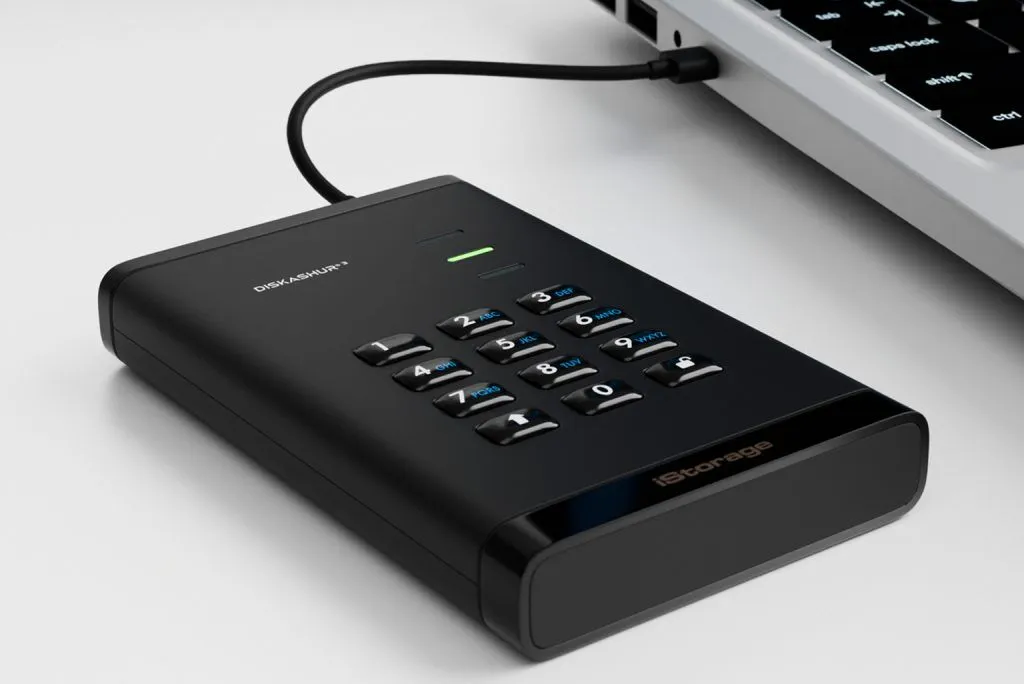

iStorage diskAshur3: A solid choice for secure portable storage [Review]
While cloud storage offers convenience and accessibility, it may not always provide the level of security some users require, especially if you have private data that you can’t afford to have fall into the wrong hands. If security is paramount, you should definitely consider a PIN authenticated hardware encrypted portable USB drive like iStorage’s excellent diskAshur3.
Available with HDD and SDD storage in a choice of capacities, diskAshur3 is designed with portability in mind, Measuring just 130mm x 80mm x 20mm, its sleek and sturdy build makes it easy to carry, whether you're traveling for business or managing data on the go. The device is compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iPadOS and more. It comes with both USB Type-A and Type-C cables, so you can connect it to most devices. Additionally, a protective carry case is included to keep the drive safe during transport and you get a free one year license of Nero BackItUp and iStorage DriveSecurity.
Tor Browser 14.0 amps up privacy, but drops support for older Windows and macOS systems -- are you still protected?
The Tor Project has announced the release of Tor Browser 14.0 for Windows (both 32-bit and 64-bit), Mac, Linux, and Android. The browser offers increased privacy to users by redirecting their internet traffic through the open Tor network.
Tor Browser 14.0 updates the browser’s underlying code to the latest Firefox ESR release -- 128 -- while also introducing new improvements that allow its fingerprinting protections to work with several new features introduced in Firefox’s latest ESR release.
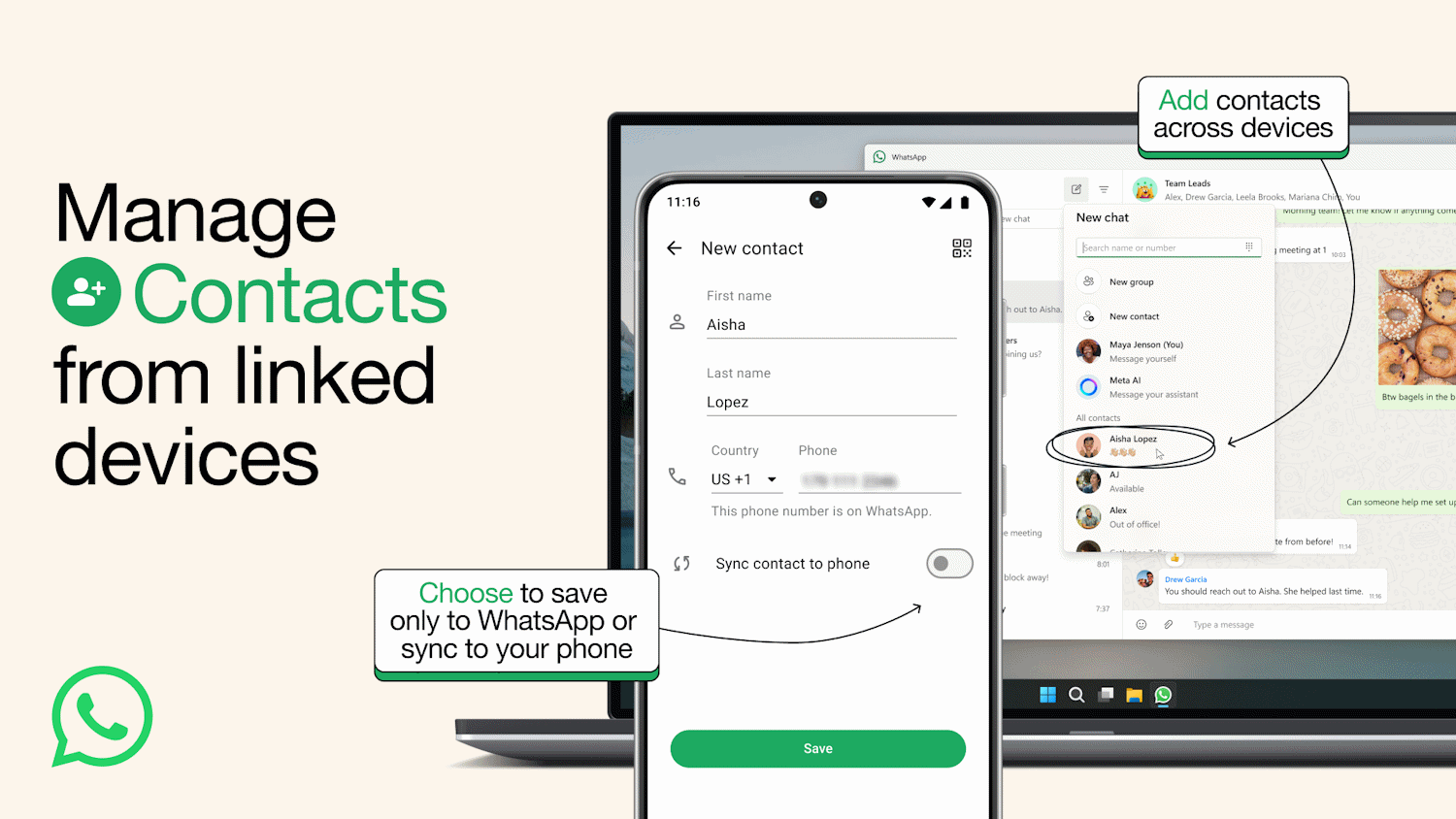
Adding contacts to WhatsApp just got a whole lot easier
Managing WhatsApp contacts has proved to be a frustrating friction point for many users, and Meta has just announced that it is taking steps to simplify things.
As well as making it possible to add contacts via the web interface and Windows app, soon it will be possible to use linked devices -- not just your primary mobile -- to manage them. There are also new privacy controls including the option to create WhatsApp-only contacts to keep your main address book separate. And there is more on the horizon, with contact usernames being a particular highlight.

Cyber resilience vs. cybersecurity: Which is more critical?
Today, it’s not ‘if’ but ‘when’ any organization will be compromised. So, while it’s essential to strengthen cybersecurity across the entire organization, it’s also imperative to plan for a significant cyber-attack and the worst-case scenario. No business can be 100 percent secure but they can be resilient. Resilience is about continuing to thrive amidst adversity. This is why cyber resilience can be more important than cybersecurity. Every organization can take positive actions to improve their cyber resilience today, ensuring they can continue to win even if they are affected by an incident. They can start by having the right mindset and instilling a culture of cyber security and cyber resilience.
Strong cyber resilience will enable an organization to continue to operate key business processes, even when they are under attack. This means keeping people safe, guaranteeing data security, and protecting their reputation with their customers, partners, suppliers, industry and government regulators and other key stakeholders. Having a strong cyber resilience will save stress, time and money -- it will give you a return on your investment -- and you’ll be better prepared for uncertainty in the future.

Third-party risk and resilience in DORA
In February 2016, it was reported that threat actors exploited vulnerabilities in the SWIFT banking network to steal more than $80 million from the central bank of Bangladesh. SWIFT, the global financial system’s main electronic payment system, which processes billions of dollars of transactions every day, was unprepared for the threat of a major cyber attack. The incident served as a pivotal wake-up call for the entire financial services industry, highlighting the previously underestimated systemic risks posed by unsecured systems. It reinforced the need for stronger security controls, safeguards and a more proactive approach to cybersecurity across the sector.
Today, organizations understand that it’s a matter of when -- not if -- their organization or supply chain is targeted with a cyber attack. Threats continue to increase in sophistication and frequency, particularly when it comes to ransomware.

The increasing priority of security in data management
Data security has become a top concern for businesses across all industries. As organizations accumulate and leverage vast amounts of data to drive decision-making, the need to safeguard that information from both internal and external threats is more important than ever.
For companies managing sensitive customer information, intellectual property, or proprietary business insights, data security is no longer a negotiable priority -- it’s a critical component in strengthening your overall security strategy.

The Internet Archive suffers massive data breach affecting tens of millions of users
The Wayback Machine has suffered a colossal security incident after the Internet Archive fell victim to a huge data breach.
Data breach notification service Have I Been Pwned (HIBP) says that a 6.4GB SQL file containing registered users’ authentication information has been shared. In all, 31 million email addresses have been found to be part of the database, and tests have shown the the data is genuine.

Still running Windows 11 22H2? No more security fixes from Microsoft for you!
Following the launch of Windows 11 24H2, this week marks the release of the final updates for various other versions of Windows. This means that anyone who has yet to upgrade from Windows 11 22H2 will not receive any more security updates.
There are numerous editions of Windows 11 affected by the end-of-service, specifically Windows 11 Home, Pro, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations and SE. The same is true for Windows 11 21H2 Enterprise, Education and IoT Enterprise, none of which will receive further updates. So, what does this mean for users?

Google removes Kaspersky apps from its store
Google has unceremoniously evicted Kaspersky’s apps from the Play Store. While the Russian security firm insists that the removal is temporary, it comes after the company’s software was banded from being sold in the US.
The move not only means that it is no longer possible to download Kaspersky apps from Google store, but also that existing users are unable to obtain updates. Google did announce the removals ahead of time.

Building a security-first culture for MSPs: Always ready, always protected
For IT professionals and MSPs, a company’s security posture is influenced not only by technology but also by its team's daily actions. Whether intentional or accidental, human behavior plays a significant role in either fortifying or undermining security measures.
Verizon Business’ 2024 Data Breach Investigation Report revealed that 68 percent of breaches this year involved a non-malicious human element, such as people falling for phishing schemes, mishandling sensitive information or getting tricked by a social engineering ploy.

Kaspersky users in the US find themselves forcibly migrated to the mysterious UltraAV
It is not unusual for software to update itself without user interaction; when it comes to delivering security patches and new features this is entirely desirable. But to have an app uninstall itself and replace itself with a different product? That’s not only highly unusually, it’s also worrying.
And yet this is what is happening for users of Kaspersky antivirus software in the US. Having been deemed a threat to national security, the sale of software from the Russian cybersecurity firm Kaspersky was banned in the US. Having promised that its customers would be taken care of, Kaspersky is now keeping its promise but forcibly replacing its security software with the largely unknown UltraAV on US customers’ computers

Save $17! Get 'Not with a Bug, But with a Sticker' for FREE
In Not With A Bug, But With A Sticker: Attacks on Machine Learning Systems and What To Do About Them, a team of distinguished adversarial machine learning researchers deliver a riveting account of the most significant risk to currently deployed artificial intelligence systems: cybersecurity threats. The authors take you on a sweeping tour -- from inside secretive government organizations to academic workshops at ski chalets to Google’s cafeteria -- recounting how major AI systems remain vulnerable to the exploits of bad actors of all stripes.
Based on hundreds of interviews of academic researchers, policy makers, business leaders and national security experts, the authors compile the complex science of attacking AI systems with color and flourish and provide a front row seat to those who championed this change. Grounded in real world examples of previous attacks, you will learn how adversaries can upend the reliability of otherwise robust AI systems with straightforward exploits.

The five stages of vulnerability management
Nearly every organization today builds a lot of software, and the majority of that software is developed by cobbling together open source components. When using open source and trying a software composition analysis (SCA) scanner for the first time, it is not uncommon for those organizations to be surprised at what they learn about their open source usage. Many times it quickly comes to light that they have a large load of new and unplanned work to address in the form of security issues in dependencies. They need to fix these issues not just for the organization itself but also to stay compliant with certifications such as PCI or SOC2.
That’s when these organizations begin to experience the five stages of vulnerability management.

Why early detection of software vulnerabilities saves time and money
Modern software development teams are under so much pressure to deliver fast. Unfortunately, speed can mean security gets overlooked during development. Fixing these issues later in the development cycle, or worse, after the software has been released, can be time-consuming, expensive and damaging to a company’s reputation. That’s where early detection of software vulnerabilities comes in. By finding and fixing these issues early organizations can save time, reduce costs and protect their users from security breaches.
In this post, we’ll look at why early detection is key, how it impacts development timelines and budgets and how security in the early stages of software development is the key to both secure and efficient software delivery.
