
Fewer than half of IT leaders confident in their IoT security
A new survey from Viakoo shows that only 50 percent of IT leaders are confident in their Internet of Things security and that 55 percent of IoT cyber incidents could have been prevented with better security measures.
In addition 71 percent say they wish they had started their IoT security efforts differently in order to remediate issues faster.

A smarter society, rise of the robots and security worries -- Internet of Things predictions for 2024
With ever increasing numbers of smart devices in our homes and workplaces, the Internet of Things has become an established facet of everyday life.
But like the rest of the technology industry the IoT isn't standing still. Here are some expert views on the opportunities and risks it's likely to present in 2024.

Building an effective and insurable IoT security policy [Q&A]
As businesses look to manage their cybersecurity risk, many have turned to insurance to cover the financial implications of a successful breach.
However, insurers naturally want to limit their own exposure to risk and the small print of the policy may limit some claims. In particular this can apply to IoT devices which represent a major unprotected attack surface in corporate networks.

Businesses struggle with IoT device connectivity
A new report finds that IoT success is being jeopardized with just one percent of respondents achieving better than 98 percent connectivity levels on average across their devices.
The study, by connectivity solutions specialist Eseye, shows that only 16 percent of respondents are achieving more than 95 percent connectivity. Mission-critical IoT devices -- medical equipment for example -- require near-100 percent connectivity and the fact that companies are prepared to accept poor performance is concerning.
AI solutions for IoT security: How Artificial Intelligence protects low-resource devices
IoT devices are created to perform specific functions, so their technical specs are naturally quite limited. They are unlike smartphones or tablet computers that come with powerful processors and large data storage. Putting traditional security mechanisms like encryption and intrusion detection systems on these devices is impractical. Installing full-fledged security solutions in them is out of the question, let alone AI-powered systems.
However, this does not mean that AI cannot be used to secure IoT devices or entire IoT ecosystems. Here’s a rundown of how AI solutions for IoT are harnessing the benefits of AI to protect IoT and other low-resource devices, including actuators, sensors, wearables, and microcontrollers.

Empowering the partner ecosystem: How businesses can gain resilience connectivity
In today's networked economy, the ability to create value depends primarily on the relationships built with other firms. As a result, strategic and product-related decision-making becomes increasingly complex. This is because a business is viewed as a component of a broader economic ecosystem and environment, where it influences and is influenced by other partners, suppliers, and organizations.
Within a business ecosystem, firms collaboratively and competitively develop innovations and capabilities where they have the capacity and freedom to do so. This enables them to support new products, meet customer needs, and incorporate subsequent waves of further innovation. Platform-based technology frequently supports these ecosystems, serving as foundations for products and services. Suppose businesses want the ability to facilitate transactions between distinct groups of users in a two or multi-sided market. To do this, they need connectivity infrastructure that is robust and reliable enough to support it alongside partners that can enable it.

IoT and digital replicas: Powering up innovation with digital twins
The concept of digital twinning isn’t a new one. More than 40 years ago, NASA used an early form of digital twin technology to bring the Apollo 13 astronauts safely back to Earth. By replicating the real-life conditions of the crippled spacecraft in its simulators, NASA was able to identify the right strategies and procedures for achieving a successful return in the damaged craft and deliver this critical information to Apollo’s flight crew.
Fast forward to today, and digital twin applications are now being deployed by organizations eager to harness the power of virtual prototyping to reinvent their operations. All made possible by the growing prevalence of IoT devices that pull real-time data collected from physical objects, which is used to create digital twins that deliver unprecedented visibility into assets and production processes.

Creating digital workplaces with IT, AI and IoT
Due to the many advances and new developments in technology, the way in which businesses are communicating is changing. Technology holds a central role in reshaping how employees work, interact and engage with others. This is helping to create digital workplaces, where emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are powering organizations to utilize data and increase access to information.
While technology such as AI and automation have been in existence for some time, the speed and rate of adoption across the business landscape is gathering pace as a means to digitize workplace settings. Currently, 15 percent of all UK businesses have adopted at least one AI technology, with the IT and telecommunications sector leading the way with the highest rate of adoption at 29.5 percent. But what features and technologies matter most to end users and how is this evolving across the digital workplace?

How businesses can overcome IoT device firmware skills shortages
In recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become an increasingly important area for businesses as more and more companies look to connect their products and services to the internet to deliver new experiences and unlock new revenue streams and capabilities. In Eseye's Annual State of IoT Adoption survey, over three-quarters (76 percent) of respondents said that IoT is a priority for their business in the next two to three years.
However, the design of hardware, firmware, and coding connectivity management software into IoT devices are all highly specialist areas. These three core components require significant specialized knowledge and expertise. A considerable skills gap in the industry makes it difficult for businesses to successfully design, develop, and deploy IoT estates.

Why organizations must not overlook connectivity design before rushing IoT devices to market
Spurred on by the dramatic shift in the global economy, the acceleration of digital transformation triggered a rise in new technologies appearing on the market. As a result, businesses have responded fiercely, scaling IoT initiatives rapidly, with mixed results.
With growing interruptions in workflow due to poor connectivity, integration, and supply chain issues, organizations have had to cope with a long list of challenges when deploying IoT to market. This has included the drive to cut costs, adhere to ever-tighter deadlines, and plug the ongoing engineering skills shortage gap.
Cheaper sensors, privacy challenges and stronger standards -- Internet of Things predictions for 2023
As more everyday devices gain connectivity features the Internet of Things is increasingly a part of everyone's lives.
Like any new technology it brings challenges around privacy and security, as well as placing additional demands on networks and data handling. Here is what some experts think we'll see from the IoT in 2023.

What are the most successful areas of tech in 2022?
Technology has evolved quickly in the past few decades and its growth has shown no signs of slowing down anytime soon.
Some trends come and go, but others stay as a way to solve catastrophic issues. These five areas of tech have been the most successful in 2022 and will be a mainstay for decades to come.

Industrial systems under threat from wipers and IoT botnets
The latest OT/IoT security report from Nozomi Networks shows that wiper malware and IoT botnets dominate threats to industrial control systems.
Researchers have observed the robust usage of wiper malware, and seen the emergence of an Industroyer variant, dubbed Industroyer2, developed to misuse the IEC-104 protocol, which is commonly used in industrial environments.
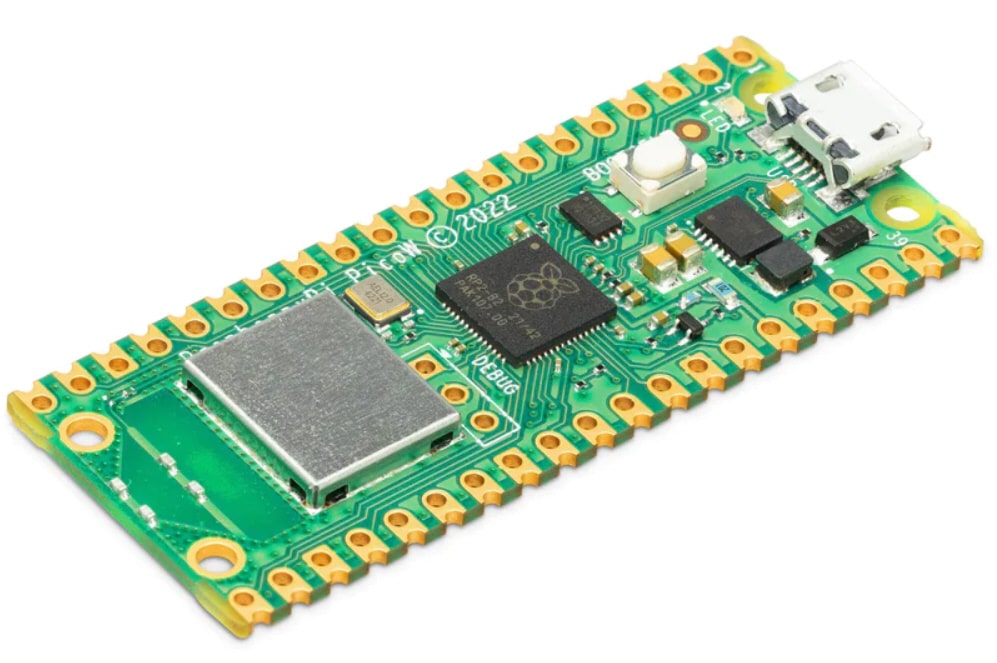
Raspberry Pi Pico W is a $6 wireless-enabled microcontroller for IoT projects
A year ago, the Raspberry Pi Foundation unveiled the Raspberry Pi Pico, a $4 microcontroller designed for physical computing projects. Easily programmed using MicroPython, it was designed for tasks like controlling lights, buttons, sensors, motors, and even other microcontrollers.
Today, after having sold nearly two million Pico boards, the Foundation announces the Raspberry Pi Pico W which adds 802.11n wireless networking to the platform.
How IoT connectivity is reaching new heights
IoT solutions utilizing SIM-based cellular technology for connectivity are not new -- but the speed with which IoT is expanding, embracing ever more exciting and dynamic use cases is both compelling and creating market confusion in equal measure. From a market which is reaching maturity -- the standardized, tried and tested, M2M SIM IoT deployments -- to one (e.g. 5G SIM-based IoT) which is largely in its infancy, separating between those solutions that can be bought with confidence and those where continued innovation warrants discussion and consultation, may not be straightforward. And, for these latter cases, choosing the right cellular (SIM) technology and network type will require an understanding of the technical requirements for each use case and the data profile of the asset to be connected.
With the definition of IoT expanding almost daily and suppliers increasingly jumping on the IoT bandwagon, this is a complex landscape, requiring knowledge, understanding, and expert partnerships. Nick Sacke, Head of IoT Solutions, Comms365 explains how to navigate the maze of options to optimise and future proof your cellular IoT investments.
