
How the metaverse is set to change the way businesses communicate [Q&A]
Increased use of the metaverse and other immersive spaces using VR, AR and digital avatars, is going to change how businesses communicate with their customers.
In an increasingly globalized world part of the issue is how real time experience will cope with the use of different languages. This is expected to put real pressure on automated and machine translation services to deliver fast, accurate results.
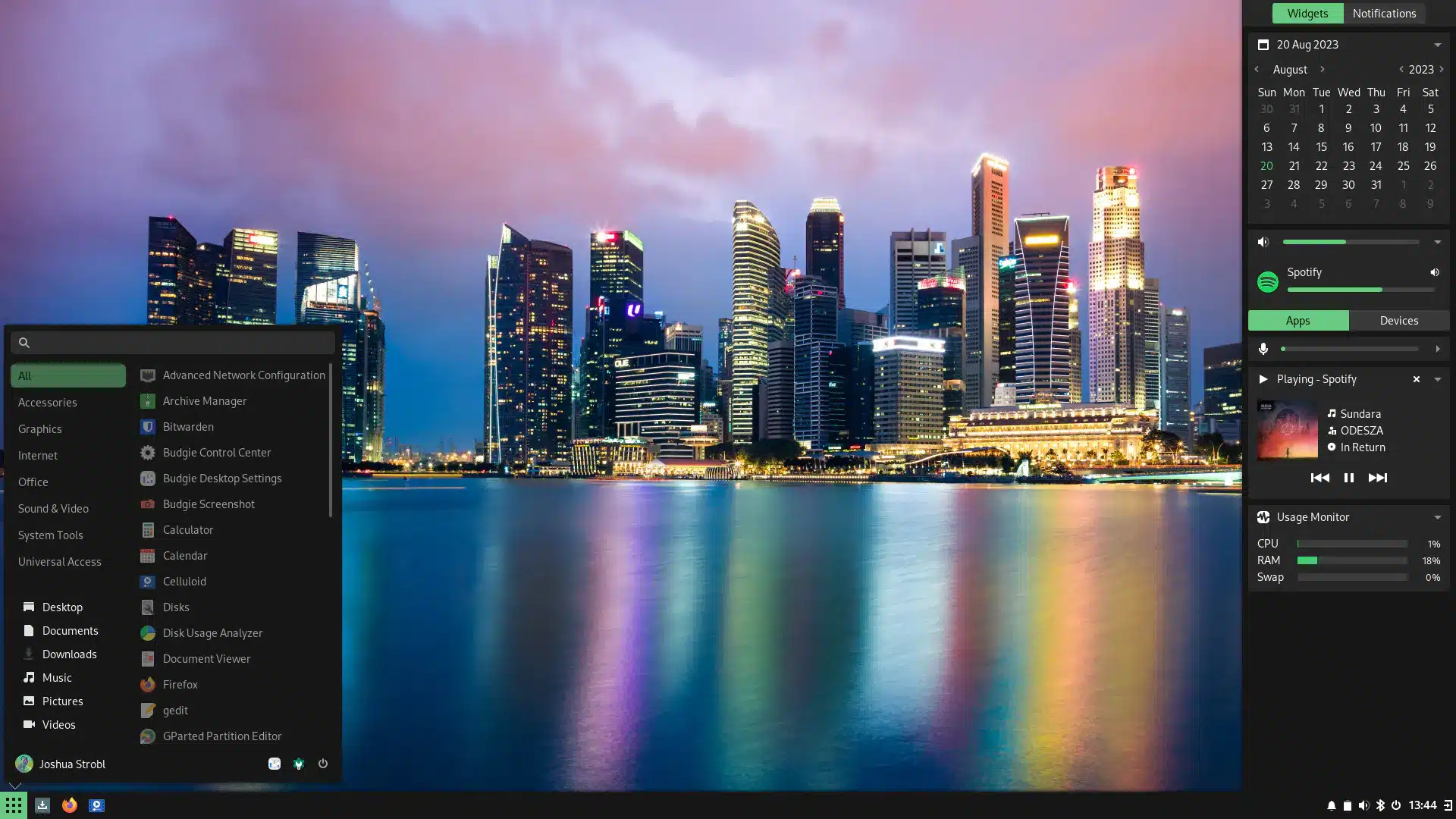

Budgie 10.8 takes Linux desktop experience to new heights
Exciting news, y’all! Budgie 10.8 has landed, and the Linux desktop environment is packed with features that promise to transform how we interact with our desktops.
First off, the Budgie Menu has received quite the makeover. If you've ever scratched your head wondering why certain apps are in the 'Other' category, you're not alone. The team listened to feedback, and now, applications have found more fitting categories. Plus, there’s a nifty fix for non-Latin text crashes, thanks to a switch to C for the Application Indexer's fuzzy scoring function. And, let's say goodbye to the Utilities category; its apps have found a new home in System Tools.

From garage to global giant: The evolution of Apple
Apple Inc., the brainchild of Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, has transformed from a humble garage start-up into a global technology powerhouse since its inception on April 1, 1976. The trio's vision was to develop and sell personal computers, with their first offering being the Apple I, hand-built entirely by Wozniak and marketed by Jobs.
Introduced at the Homebrew Computer Club in Palo Alto, California, the Apple I marked the beginning of a technological revolution. Despite the company's modest beginnings, its vision was clear -- to bring an easy-to-use computer to the market. In 1977, Apple was incorporated without Wayne, who sold his share back to Jobs and Wozniak for $800. The same year, the company launched the Apple II at the West Coast Computer Faire, propelling Apple into the forefront of the burgeoning personal computer industry.
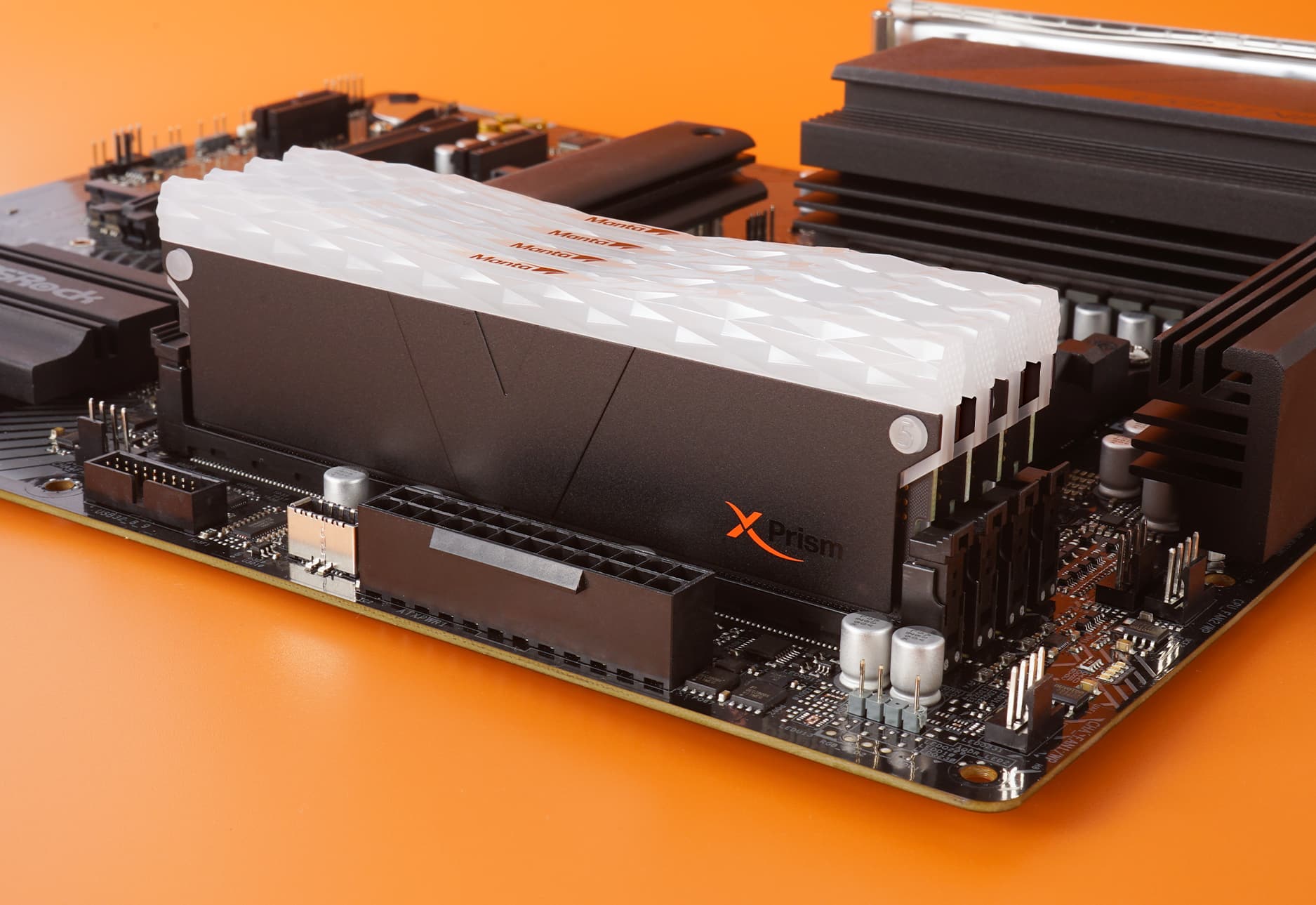

V-Color announces MANTA XPrism RGB DDR5 48GB (2x24GB) Memory Kit
Hey there, fellow tech nerds! So, V-Color's at it again, rolling out another piece of kit. This time, the company announces the MANTA XPrism RGB DDR5 48GB (2x24GB) Memory Kit. This RAM should be available here later this month. Pricing is not yet known, sadly. It comes in this SCC 2+2 setup and touts speeds that swing between 6200 to 6600.
V-Color has thrown in its patented RGB Filler Kit, which they say is perfect for Intel systems. They're also hyping up its Intel XMP 3.0 compatibility for smooth automatic overclocking. And guess what? They claim it'll play nice with some of the big motherboard names like ASUS and GIGABYTE.

Update WinRAR right now to patch high-severity security flaw
Users of the archiving utility WinRAR are being advised to update their software as soon as possible following the discovery of a serious Remote Code Execution vulnerability.
Tracked as CVE-2023-40477, the security flaw was discovered back in June and it allows malicious code to run when opening a RAR archive. Two months on, the issue has been fixed, but users of the software will have to ensure that they have the latest update installed to guarantee protection.

What to look for in a third-party vendor while cutting budgets
At the end of 2022, many companies (83 percent) feared a recession in 2023, with 60 percent of enterprise-level and 45 percent of SMB-level businesses preparing by tightening budgets, reducing non-essential spending, renegotiating payment terms and other strategies. Yet SWZD’s 2023 State of IT Report also found that over 50 percent of companies planned to increase YOY IT spending, with budgets expected to grow 13 percent YOY.
That same report indicated that 23 percent of companies had already implemented -- or planned to form -- strategic partnerships.

Google's journey: From Stanford to Silicon Valley -- a revolution in the digital world
The history of Google, a company that has significantly transformed the digital world, is an inspiring tale of innovation, ambition and an unyielding quest for information. The story unfolds in the heart of Silicon Valley, California, in 1996, where two Stanford University students, Sergey Brin, a Russian immigrant, and Larry Page, crossed paths. Brin was tasked with showing Page around the university.
Despite some initial disagreements, they found common ground in their shared passion for data mining and retrieval. This shared interest would eventually lead to the creation of a search engine that revolutionized the way people interact with the internet.

74 percent of cloud and web applications with PII are vulnerable to exploits
New research reveals a high proportion of vulnerable public cloud, mobile and web applications exposing sensitive data, including unsecured APIs and personal identifiable information (PII).
The study from CyCognito, based on analysis of 3.5 million assets across its enterprise customer base, finds 74 percent of assets with PII are vulnerable to at least one known major exploit, and one in 10 have at least one easily exploitable issue.

Looking over the edge -- how edge computing will impact business decisions [Q&A]
Earlier this year, AT&T's Cybersecurity Insights Report found that business and technology leaders are finally coming together not just to understand the new edge computing ecosystem, but to make more predictable, data-informed business decisions.
We spoke to head of cybersecurity evangelism at AT&T Business, Theresa Lanowitz, to find out more about the edge journey ahead and how it will affect businesses.

Best Windows apps this week
Five-hundred-and-fifty-six in a series. Welcome to this week's overview of the best apps, games and extensions released for Windows 10 and 11 on the Microsoft Store and elsewhere in the past seven days.
Windows 11 users may soon uninstall more native applications. Microsoft unlocked the apps Camera, Cortana, Photos, People and Remote Desktop (MSTSC) in the latest development builds.

PNY DUO LINK iOS USB 3.2 Flash Drive: The ultimate storage solution for Apple iPhone
In a world increasingly dominated by mobile devices, the ability to manage and transfer data effortlessly across platforms is crucial. PNY's DUO LINK iOS drive absolutely rises to this challenge. With a Lightning connector tailored for iOS devices and a USB 3.2 Type-A connector for broader compatibility, the DUO LINK ensures that file transfers are not just limited to one platform.
With the DUO LINK iOS drive, gone are the days of frantically searching for storage space during a critical moment or a valuable photo op. The drive provides instant access to your media, allowing you to save precious content on the go. It elegantly removes the need to juggle multiple devices, making travel or day-to-day commuting a breeze.
The future of AI lies in open source
I'm almost getting sick of hearing about AI and its ability to change the world for the better, for the worse, for who knows what? But when you get to the heart of what AI is and how it can be applied to unlock value in businesses and everyday life, you have to admit that we're standing on the edge of a revolution. This revolution is likely to change our lives significantly in the short term, and perhaps tremendously so in the medium term.
It wasn't that long ago I felt short-sold by the promise of AI. About eight years ago I saw someone demonstrating a machine's ability to recognize certain flowers. Although impressive, it was a clunky experience, and while I could imagine applications, it didn't excite me. Fast forward a few years, my real moment of surprise came when I found thispersondoesnotexist. My brain couldn't work out why these were not real people, and it stuck with me. My next big moment was podcast.ai and their first AI generated discussion between Joe Rogan and Steve Jobs. But just like everyone else on the planet, the real breakthrough was ChatGPT and the conversation I had with the 'Ghost in the Machine'.
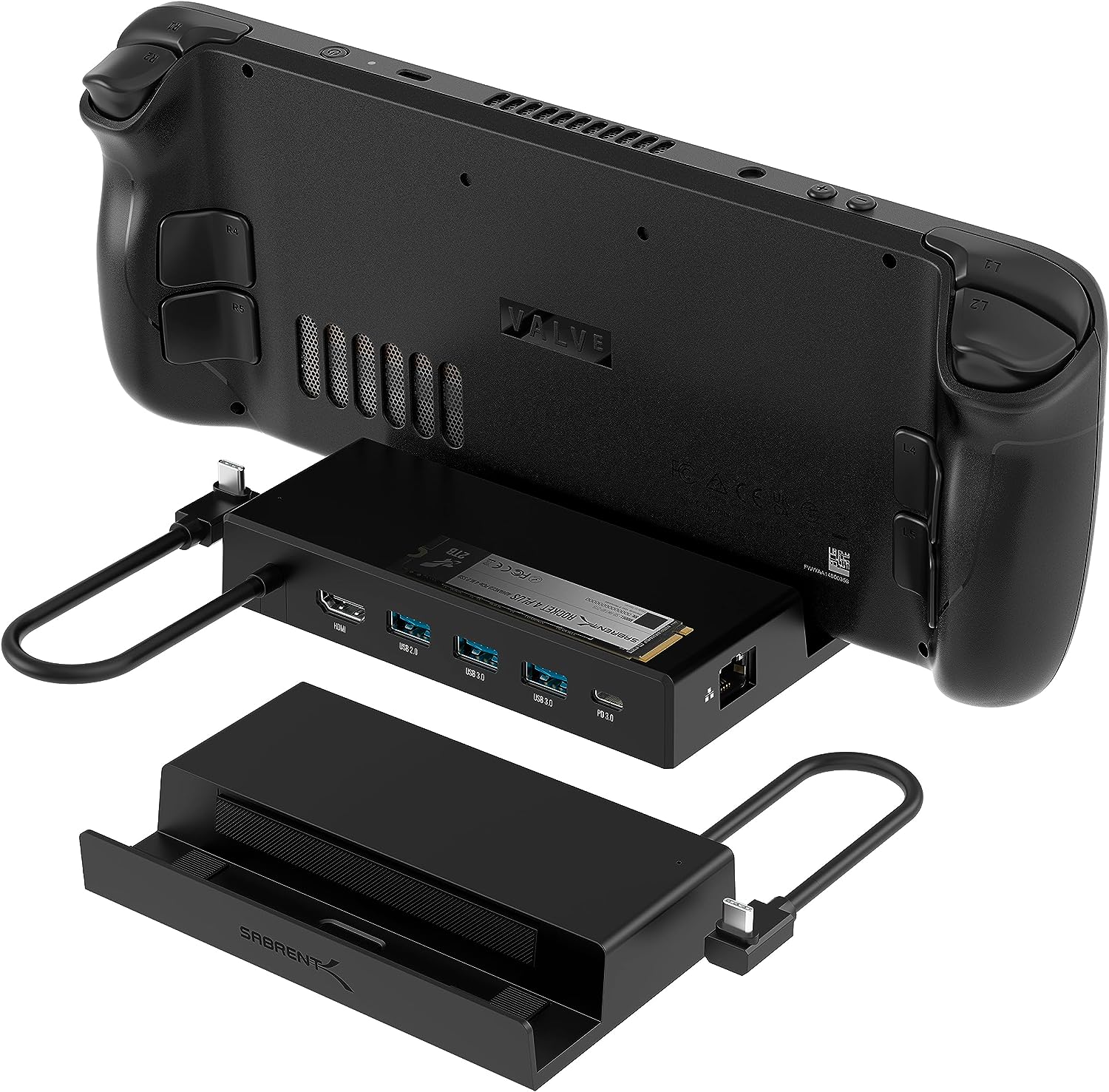

Sabrent USB-C Docking Station with M.2 Port (DS-SDNV) is the ultimate dock for Steam Deck and ASUS ROG Ally
When it comes to docks, we often seek versatility and capability in one neat package. Enter the Sabrent USB Type-C 6-Port Docking Station with M.2 Port (DS-SDNV). This isn’t just any dock; it’s an all-in-one solution for your Steam Deck, ROG Ally, and other USB-C devices.
The DS-SDNV isn’t picky about operating systems. Whether you’re on Windows, Linux, or macOS, it’s got your back. If you have USB-C devices with DisplayPort Alternate (DP Alt) Mode support, you can harness the power of HDMI 2.0 (HDCP 1.4) for seamless output.

How financial services cyber regulations are hotting up for API security
Financial services firms deploy an increasingly complicated mix of technologies, systems, applications, and processes to serve customers and partners and to solve organizational challenges. Focused heavily on consumer hyper-personalization, banks are evolving more and more digital assets and services to meet and exceed growing customer experience expectations.
As a result, the modern banking environment is heavily reliant on APIs to the point that they are now indispensable. APIs allow financial banks to connect with their ecosystem, while inspiring innovative developers to create new products, improve existing services, and work more efficiently.
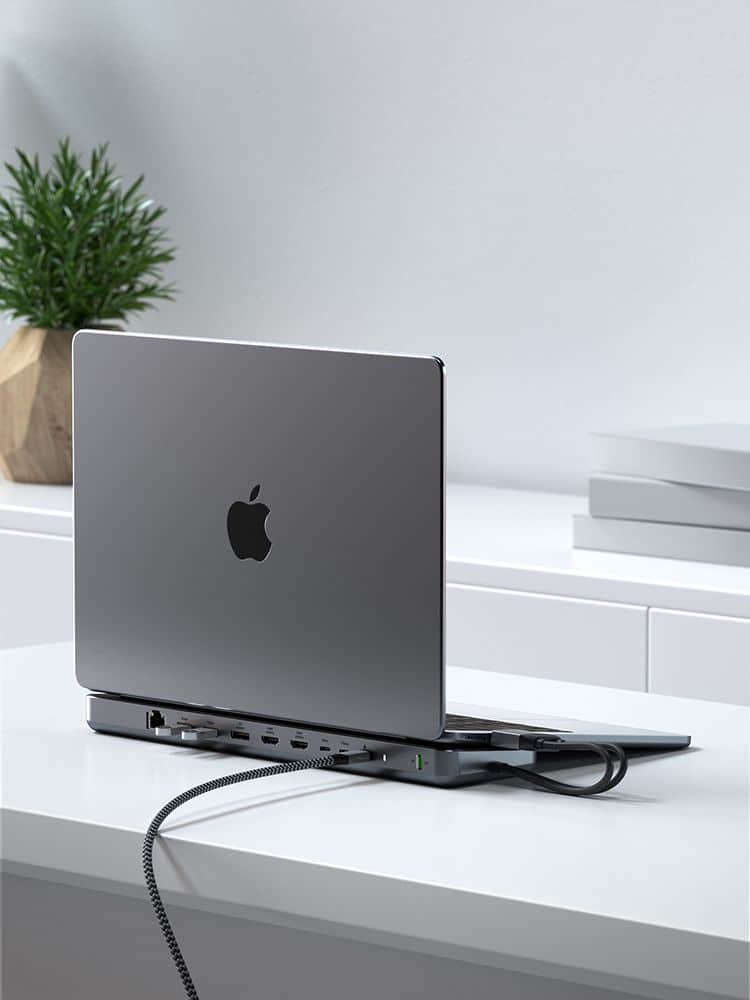

Satechi Dual Dock Stand provides NVMe SSD storage and multi-screen flexibility
Today, Satechi launches its newest product, the Dual Dock Stand – a fusion of a docking station with an NVMe SSD Enclosure. The Dual Dock can transform an Apple MacBook or Windows laptop into a makeshift desktop. The stand, built from robust aluminum, sports a space-gray and black finish.
The Dual Dock Stand boasts two HDMI ports and a DisplayPort, allowing users the flexibility to expand their screen capacity with a crisp 4K/60Hz resolution. This expansion can accommodate up to two monitors, although those with Mac M1/M2 systems should note the limitation of just one external display.



