How decentralized storage can help prevent data breaches [Q&A]
According to a recent IBM report the average cost of a data breach is now $4.35 million. If enterprises don't take steps to protect personal data effectively they risk losing not just money but also the trust of their customers.
We spoke to Saswata Basu, founder and CEO of 0Chain, to discuss how decentralized storage can help to address the problem.

Evervault is offering free encryption services to women's health apps
There have been several knock-on effects from the Supreme Court ruling on Roe v Wade, but few people would have predicted a change in app use habits out of fear of criminal proceedings. But this is precisely what has happened as growing numbers of users are concerned about the potential for data stored in apps to be used against them
It's just one of the reasons there has been numerous instances of users either ditching period tracking apps altogether, or switching to options considered to be more secure. Now encryption firm Evervault has offered up another solution, announcing it will offer its encryption services free of charge to women's health apps.

Almost half of UK organizations now encrypt all their data
The increasing threat of data breaches and ransomware is leading more business to encrypt all of their data according to a new report.
The report, from hardware-encrypted USB drive maker Apricorn, is based on a study of 100 UK IT decision makers carried out by Vanson Bourne and finds 47 percent now require the encryption of all data both at rest and in transit.

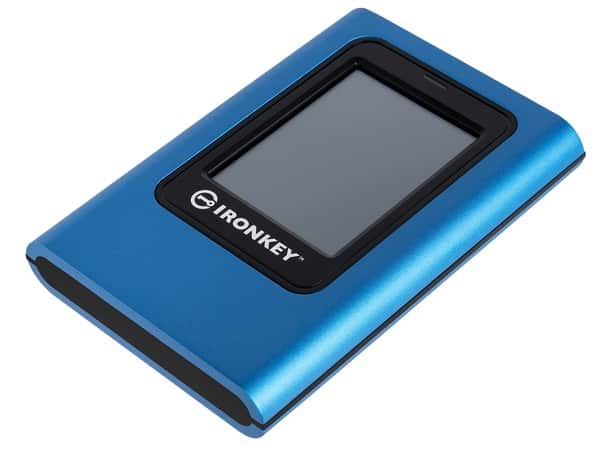
Kingston releases hardware-encrypted IronKey Vault Privacy 50 USB flash drive
We recently told you about the Kingston VP80ES IronKey Vault Privacy 80 -- a speedy portable SSD that features USB-C connectivity and a touchscreen for tapping-in a password or pin. While that drive is quite amazing, not everyone will truly need the fast speeds or touchscreen -- it could be overkill. Instead, a hardware-encrypted USB flash drive could be sufficient -- and much less expensive.
Today, Kingston launches its latest hardware-encrypted flash drive. Called "IronKey Vault Privacy 50 (VP50)," the drive uses a USB-A connector and is offered in capacities ranging from 8GB to 256GB. The VP50 features XTS-AES 256-bit encryption and is FIPS 197 certified.

The role of encrypted traffic analysis for threat detection [Q&A]
Everyone is striving to make their systems more secure and in many cases that means adopting encryption in order to protect data.
But the use of encrypted traffic over networks presents a headache for security teams as malicious content can be harder to detect. We spoke to Thomas Pore, director of security products at Live Action, to find out more about the problem and how it can be addressed.

Kingston VP80ES IronKey Vault Privacy 80 is an encrypted USB-C SSD with touchscreen
Solid state drives don't just make wonderful internal boot drives for computers -- they're excellent for external storage too. Not only are they smaller than mechanical hard disk drives, but they use less power and are much faster as well. Quite frankly, if you are someone that needs to transport data on a portable drive, you'd be insane to still use a HDD with moving parts.
But what if you lose that external solid state drive? Well, if the content is unencrypted, your files could be exposed to the finder. This is particularly problematic for business users that are storing company secrets or private customer data. Thankfully, a new USB-C solid state drive from Kingston makes it super easy to encrypt and decrypt your data. You see, the VP80ES IronKey Vault Privacy 80 is a hardware-encrypted (FIPS 197 certified with XTS-AES 256-bit) SSD with a color touchscreen that allows you to enter a passcode, password, pin, or phrase.

New solution aims to address quantum security threats
We all know that quantum computing is going to offer a major boost in computing power. But that power also represents a threat to cryptographic systems, potentially putting the world's data at risk.
To address the issue QuSecure is launching an industry first end-to-end post-quantum cybersecurity (PQC) software-based solution designed to protect encrypted communications and data with quantum-resilience.

Enterprises poorly protected against third-party risks
A new report from compliance and risk management firm Kiteworks shows 51 percent of organizations are inadequately protected against third-party security and compliance risks related to sensitive content communications.
It also reveals that most organizations share sensitive content with a long list of third-party entities. Two-thirds do so with more than 1,000 third parties, while one-third have over 2,500.

Why PKI still has a key role in security [Q&A]
The origins of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) date back to the 1970s and research at UK intelligence agency GCHQ, though it didn't emerge from the secret world and take off commercially until the 1990s.
PKI still underlies a great deal of modern cryptography, so we spoke to Ryan Sanders, senior product marketing manager at Keyfactor, to find out more about it and why it isn’t going away any time soon.

The internet is getting safer but legacy encryption techniques still linger
A new report from Venafi, based on in-depth security analysis of the world's top million websites over the last 18 months, shows the internet is becoming more secure.
Use of encryption is increasing and the adoption of newer TLS protocols is rising. However, many companies continue to use legacy RSA encryption algorithms to generate keys, despite stronger protocols being available.
Google Fi gets end-to-end encryption for phone calls, but there's a big catch
Google Fi is the search giant's affordable MVNO cellular service, where it piggybacks off of the T-Mobile and U.S. Cellular networks. Despite being a Google service, it is actually compatible with Apple iPhone devices too. In other words, it is not an Android-only affair. While Google Fi is not wildly popular, many of its users speak favorably of the service -- it is apparently quite good.
And now, Google Fi is getting even better. You see, the search giant has introduced end-to-end encryption for phone calls -- a huge benefit for privacy. Unfortunately, there are some caveats here. For the calls to be encrypted, the speakers on the call must both be using Google Fi service -- that should be fairly obvious. However, there is one very big catch that might surprise you -- this feature is only compatible with Android devices. In other words, iPhone users with Google Fi are being left out of the encryption party.

Revealing the industries most hit by ransomware
New research from cloud encryption specialist NordLocker looks at which industries are the most popular targets for ransomware, analyzing 1,200 companies hit by 10 infamous ransomware gangs in 2020 and 2021.
Perhaps surprisingly the construction sector tops the list with 93 attacks, followed by manufacturing on 86, finance on 69, healthcare on 65, and with education rounding out the top five on 63.

New cryptography solution aims for 'cyber herd immunity'
Increased reliance on digital systems and remote workforces has drastically increased the attack surface threatening to compromise organizations.
Encrypting information is part of the solution but is still vulnerable if keys fall into the wrong hands. Now though Australian deep tech cybersecurity start-up Tide Foundation has come up with a decentralized solution that offers the promise of 'cyber herd immunity'.

Over 90 percent of malware arrives over encrypted connections
Security experts have spent years driving home the message that HTTPS connections are safer, but a new report released today reveals that 91.5 percent of malware arrived over encrypted connections in the second quarter of this year.
The quarterly internet security report from WatchGuard Technologies also shows alarming surges across fileless malware threats, dramatic growth in ransomware and a big increase in network attacks.

The encryption technology that's revolutionizing secure data usage [Q&A]
Conventional encryption methods rely on the exchange of keys. This can leave them vulnerable, particularly when they're used on public cloud services.
One way around this is to use homomorphic encryption, this permits third party service providers to perform some types of operations on a user's data without needing to decrypt it.
