
Quantum computing and its impact on cybersecurity [Q&A]
Quantum computing with its vastly improved processing capability offers the chance of many positive developments in research and science. But it also represents a potential threat to our current encryption models.
How big is quantum's threat to cybersecurity? And should we be taking action on this now? We talked to Skip Sanzeri, QuSecure co-founder and COO, to find out.

More than half of enterprises worried about supply chain risks
Software supply chain risk has become mainstream, with 52 percent of respondents to a new survey being concerned about it.
The study from cybersecurity company Coalfire also finds 50 percent of boards of directors with software-buying companies are raising concerns, which means that responsibility for software supply chain risk is no longer confined to technical teams.

Research reveals weaknesses in five popular web services
New research from Specops Software finds major cybersecurity weaknesses in popular web services including Shopify, Zendesk, Trello, and Stack Overflow.
The study shows several popular business web applications have failed to implement critical password and authentication requirements to protect customers from cybercrime.

Average cost of a data breach increases by 16 percent
A new report released today by ForgeRock shows the average cost of a breach in the US has increased by 16 percent to $9.5m, making the US the costliest place in the world to recover from a breach.
It also reveals a massive 297 percent surge in breaches caused primarily by security issues associated with supply chain and third-party suppliers and representing almost 25 percent of all breaches.

Why do we continue to rely on the 'weakest link' to protect our organizations' email?
Email security continues to be a top concern of organizations, with 94 percent of all cyber attacks being delivered through email. As the most frequently used communication channel across all industries -- no wonder threat actors love exploiting it!
The conventional approach to email security is failing. Our latest research found that an average of 75 malicious messages per 100 mailboxes slip past traditional email security filters every month. Consequently, organizations put employees through countless hours of security training with hopes they spot and report these threats to security operations centers. The so-called Human Firewall.

Automation in cybersecurity: Overcoming barriers
"Automation" has become a buzzword in cybersecurity circles. That is not surprising in an environment where security specialists are in short supply and under intense pressure to defend the business against a huge variety of threats from innumerable different sources. Using technology to do at least some of the work seems like a no-brainer. Nevertheless, it seems that organizations are finding it hard to get the right approach to cybersecurity automation.
Threat Quotient conducted research last year that found resources, time and a lack of trust in outcomes are preventing companies from realizing the benefits of automation. In a recent webinar, myself, Nabil Adouani, CEO of Strange Bee and co-founder of The Hive Project, and our Global VP of Threat Intelligence Engineering Chris Jacobs discussed the current state of automation, the expectations around what automation can actually achieve, and what this means for implementation in the real world.
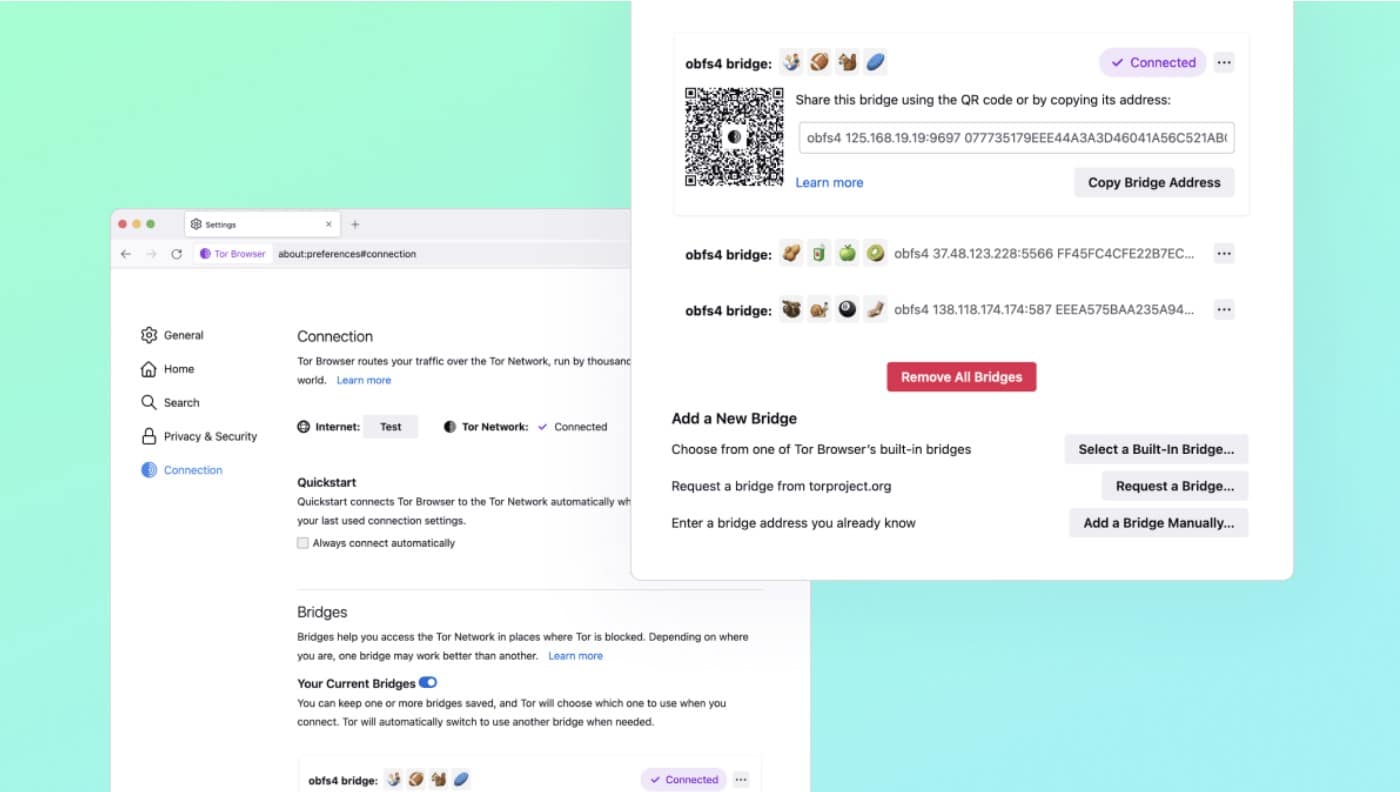
Tor Browser 11.5 is here with HTTPS-Only Mode by default and Automatic censorship circumvention
For anyone concerned about privacy and security online, Tor Browser is an extremely important alternative to mainstream browsers. Designed to help keep users anonymous and to bypass restrictions put in place by governments, version 11.5 has landed complete with even more powerful options.
Over the years, it has become easier and easier to use Tor Browser, with complex configuration options being made available to the average user without the need for special knowledge. With the release of version 11.5 of the software, things have been made even easier thanks to the introduction of automatic censorship detection and circumvention with the new Connection Assist feature.

The artificial intelligence tug-of-war in the world of cybersecurity [Q&A]
It's a rare cybersecurity product these days that doesn't claim to have some form of AI capability. But exactly what benefits does AI deliver? And is there a risk of an arms race as threat actors also turn to the technology?
We spoke to Corey Nachreiner, CSO at WatchGuard Technologies, to find out more about the role of AI in cybersecurity.

Security and automation are top priorities for IT pros
The top three priorities for IT professionals are improving IT security overall (52 percent), increasing IT productivity through automation (33 percent), and migrating to the cloud (32 percent), according to a new report.
A survey of almost 2,000 IT pros from Kaseya also reveals the main three challenges are cybersecurity and data protection (49 percent), insufficient IT budgets and resources to meet demands (29 percent), and legacy systems that hamper growth and innovation (21 percent).

Identifying key risks is top cybersecurity challenge
Risk-based strategies are most successful in preventing security breaches, according to a new study from Skybox Security.
Of companies taking a risk-based approach 48 percent suffered no breaches, 50 percent were top performers in time to mitigate issues, and 46 percent top performers in response time.

Update seems to be the hardest word as enterprises struggle to maintain endpoints
The average enterprise now manages approximately 135,000 endpoint devices. But in spite of large budgets spent on endpoint protection, an average of 48 percent of devices -- or 64,800 per enterprise -- are at risk because they are no longer detected by the organization's IT department or because operating systems have become outdated.
A new study conducted by the Ponemon Institute for Adaptiva also finds 63 percent of respondents find that the lack of visibility into endpoints is the most significant barrier to achieving a strong security posture.

Size matters -- small cybersecurity teams face greater risk of attack
Companies with small security teams continue to face a number of unique challenges that place these organizations at greater risk than larger enterprises, according to a new study.
Research from Cynet, based on responses from 200 CISOs at small and medium businesses, finds 58 percent feel their risk of attack is higher compared to enterprises, despite the fact that enterprises are a bigger target.

Majority of industrial IoT security projects end in failure
According to new research, 93 percent of organizations have had failed industrial Internet of Things or operational technology (IIoT/OT) security projects.
The study from Barracuda Networks surveyed 800 seniors staff responsible for IIoT/OT security and finds that 94 percent admit experiencing a security incident in the last 12 months, while 87 percent of organizations that experienced an incident were impacted for more than one day.

Asset visibility is a major challenge for security professionals
A new study of over 100 security professionals, carried out by unified asset intelligence platform Armis, shows almost 40 percent say asset visibility is the biggest challenge facing their organizations.
A quarter say poor asset visibility is the biggest risk and over half (54 percent) of respondents say employee behavior is a top risk.

Microsoft performs an about-face on Office macro security policy -- albeit a temporary one
VBA macros in Microsoft Office are an incredibly common means of delivering malware, and this is precisely why Microsoft made an announcement earlier this year that macros would be blocked by default. But now the company has changed its mind.
The change will not be permanent, however. Microsoft still plans to block macros in documents obtain from the internet -- it's just not quite clear when. The company says that the change of heart is a result of user feedback, and while macros will remain enabled by default for the time being, this will change at some point in the future; it's just not happening as soon as we thought.
