
Google is making it easier to get the best prices and find discount codes
Google is introducing new tools in both Chrome and Google search that should help to make online shopping a little cheaper. With the holiday season just around the corner and shoppers eager to save money, the timing is ideal.
Chrome users are gaining access to a new feature that will seek out discount codes much like services such as Honey. There is also a new section landing in search results that makes it easier to track down products that are on sale.

Google Chrome will soon offer to hide your IP address for added privacy and security
Google is preparing to launch a new Chrome feature which will give users the ability to hide their IP address. Previously known as Gnatcatcher, the feature is now called IP Protection and makes use of proxies to help prevent online tracking.
IP Protection is described as "a privacy proxy that anonymizes IP addresses for qualifying traffic". One of its primary aims is to limit the possibility for fingerprinting as a means of tracking users online, which is something that has become increasingly common as steps are taken to block, and even kill off, third-party cookies.
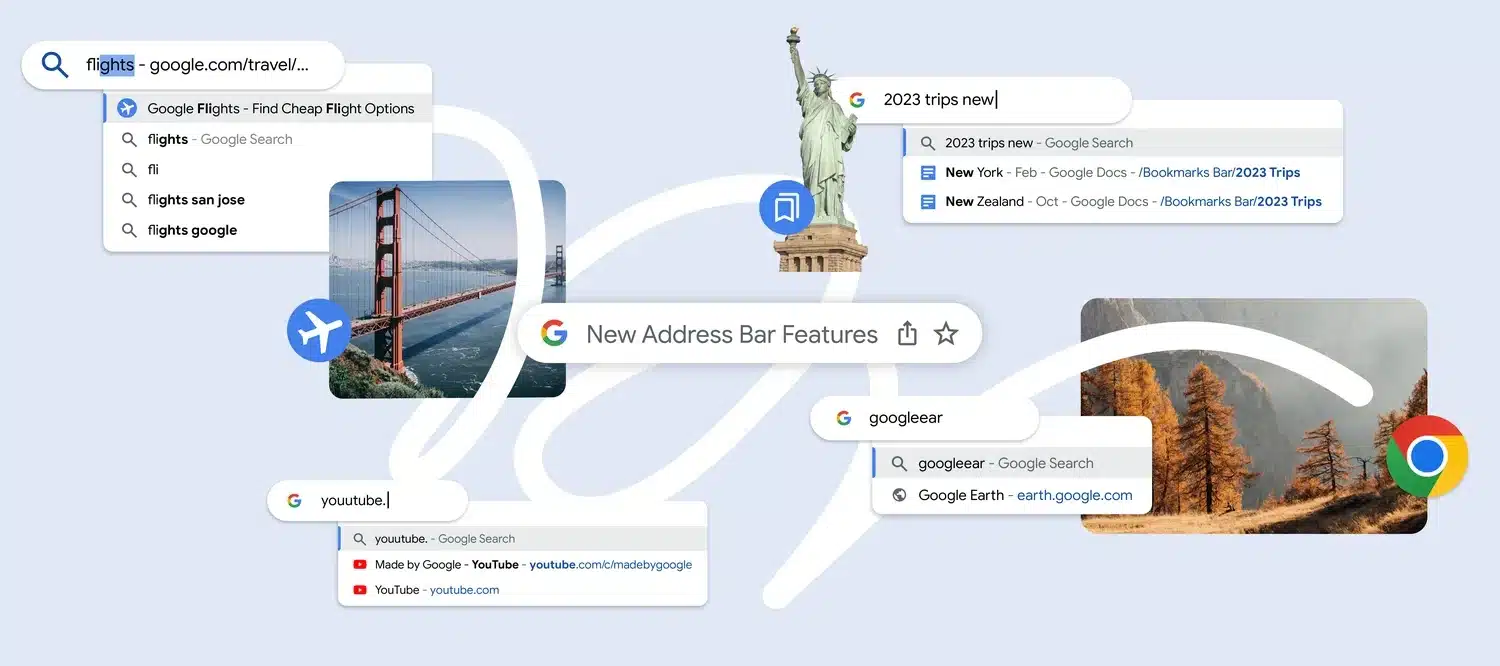
Google has a quintet of improvements to supercharge Chrome's address bar
Google has announced a number of upcoming changes to the address bar in Chrome. The company says that the five improvements will help people to browse even faster.
Some of the enhancements are long-overdue, such as updating URL autocomplete so that characters you type do not have to be the first part of the address. Others are sensible ease-of use and security-related improvements, such as automatic typo correction for typed URLs.

Microsoft Edge is snooping on your Chrome browsing activity; here's how to stop it
One web browser spying on another? Surely not! However, if you are using both Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, Microsoft's browser could be grabbing all of your browsing history from Chrome every time you launch it.
If you decided to jump from Firefox to Chrome, from Edge to Firefox, from Opera to Edge or any other combination, you will probably have taken advantage of the option to import browsing history, saved passwords and so on. But you likely don’t want this cross-browser communication to continue indefinitely. Here’s how to check whether this sneaky data swapping is happening in the background and how to stop it if it is.

Google is testing a new option so you can keep your super-recent browsing history secret
Your browsing history can be very revealing; there are countless reasons for not wanting a list of the sites you have visited to be seen by others. While it can be hard to maintain complete privacy, there are steps you can take on a local basis -- such as simply deleting your browsing history.
It is easy to see the deletion of browsing history as using a sledgehammer to crack a nut, and for a very long time it was very much an "all or nothing" approach. Over time, Google and others introduced options to limit how much browsing history should be deleted, and now Chrome users are being offered even more fine-grained controls.

Google may use AI in Chrome to organize your chaotic tabs for you
Browser tabs were introduced to help fix the problem of having too many browser windows open at once; now instead of being overrun with browser windows, we have the issue of too many tabs. Chrome's upcoming Organize Tabs feature is Google's latest attempt to tame things.
The feature is still undergoing beta testing, but when it lands it will take some of the hard work out of tab management. For anyone happy to hand control over to Google, Organize Tabs will automatically sort open tabs into appropriate Tab Groups, much like the comparable AI-driven feature already to be found in Microsoft Edge.

Google is bringing the Read Aloud feature of Microsoft Edge to Chrome
There is a great deal of copying of features and ideas in the browser world, so it can be hard to say which is "best". From Chrome and Firefox to Edge and Opera, there is so much inspiration and cross-contamination that it's difficult to find much that is unique.
The latest example of this is Google using the latest Canary build of Chrome to introduce its own version of a feature found in Microsoft Edge. Google's implementation of "Read Aloud" is near-identical to Microsoft's, but Chrome has a significantly larger user-base meaning that this handy tool will be enjoyed by more people.

Chrome password sharing feature makes it easier to share login credentials... with limitations
There are many reasons for wanting to share passwords, and it is surprising -- and also a source of irritation -- that doing so is not easier. But Google is looking to change this by introducing a dedicated password sharing option to Chrome.
Users of the browser will soon be able to use the Password Manager function of the browser to quickly share login details with others. To start with, it appears that Google will limit sharing to people you have added to your Google Family Group, but it is possible that this will be opened up further in future.

Google is switching to weekly Chrome updates to boost security
Google has announced that it will release security updates for Chrome on a weekly basis, doubling the speed with which fixes are delivered to the stable channel.
This will not change the release schedule for significant new versions of Chrome, but it means that users of the browser can enjoy greater security. Google's change in pace is designed to reduce the "patch gap", with the company saying that it treats "all critical and high severity bugs as if they will be exploited".

Google has moved downloads to the toolbar in Chrome -- but you can resist change if you want
As users of Google's web browser will be aware, Chrome has long featured a download bar at the bottom of the app window. While keeping download progress tucked out of the way made sense in some ways, it represented somewhat of a frustrating design inconsistency in moving download-related information away from the main browser controls in the toolbar.
This is something that Google had addressed in the latest update to Chrome, ditching the downloads bar with a new button in the main toolbar. While this is likely to be welcomed by most users, there will be some who prefer things how they used to be. Let's take a look at the new download button and also show you how to revert to the old approach if this is your preference.

Google is working on a new link preview feature for Chrome
It will soon be easier to check whether you want to visit a site before you click a link in Chrome. Google is currently working on bringing a new feature called Link Preview to the desktop version its web browser that will give users the ability to check out where a link leads without visiting it.
Development seems to be in the fairly early stages at the moment and while it is not yet possible to try it out, there are documents produced by the company that give a very good idea of how it will look and work.

Google Chrome's PDF viewer is gaining the ability to convert images to text
PDFs are astonishingly useful documents, but some are lazily created. You've almost certainly encountered a PDF file that comprises images of text rather than selected text. This is a serious annoyance if you were hoping to copy text into another document, but it's also a major problem for anyone who is reliant on text-to-speech tools to have document read aloud to them.
Google has some good news for users of Chrome; the browser is gaining the ability to convert images to text in PDFs, OCR-style. There is some bad news, however. This incredibly useful feature is -- at least initially -- not going to be made available to everyone.

Google Password Manager gains new features on desktop and mobile
Today, Google Password Manager, known for its ability to generate and autofill unique passwords, is introducing five new features designed to enhance security, provide helpful functionality, and ensure ease of use. The features vary from platform to platform, with some being new for desktop, while others being new to iOS.
Google Password Manager now boasts a dedicated home within Chrome on desktop platforms, providing users with a centralized location to review all saved online credentials and manage password settings. Users can easily access this feature by clicking on "Password Manager" in the Chrome menu or by selecting "Manage passwords" when prompted by Chrome to autofill a saved password. Additionally, a desktop shortcut for Google Password Manager can now be created for even quicker access.

Chrome now boasts about how much RAM its Memory Saver feature is freeing up
Chrome has long had the unenviable reputation of being a resource hog. This is something that Google has been working on over the years, and one of the most recent improvements has seen the introduction of the Memory Saver feature which puts inactive tabs to sleep to free up RAM.
With the feature enabled, you have just had to trust that it is working -- but now Google has made a change that makes it clear just how much memory is being saved by each tab. And in a future update, the browser will make it even more obvious about just how many resources it has freed up.
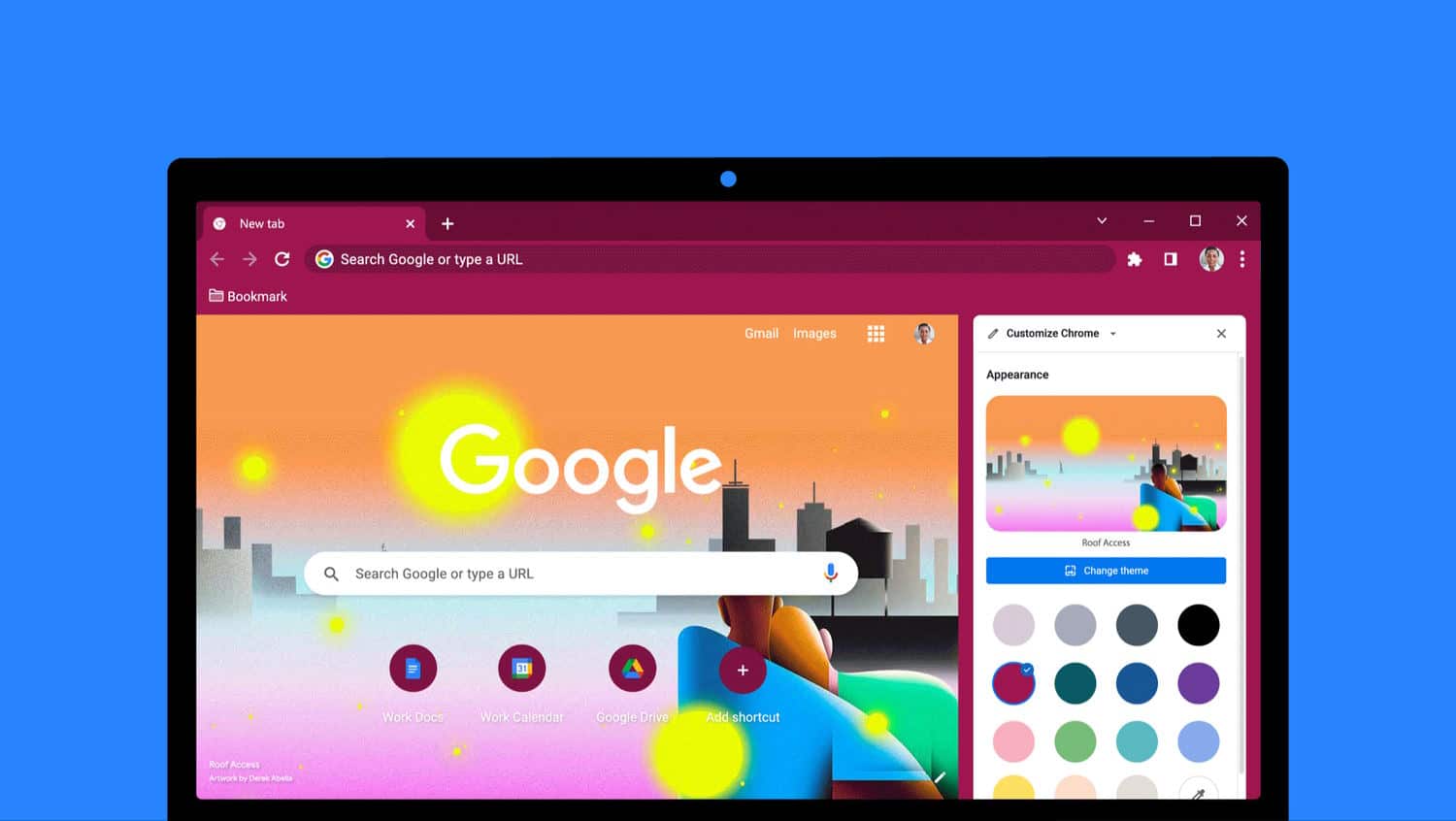
Google brings new options to Chrome so you can change the look of the browser
Google has used the latest version of Chrome to give users new ways to personalize the browser with backgrounds, themes and color schemes.
While some options, such as themes and colors, affect the entire browser, others are only visible on the New Tab page -- such as background images. Google says that it I has a wide range of "special artist collections commissioned by Asian & Pacific Islander, LGBTQ+, Latino, Black and Native American artists", and promises that more are coming later this year.
