
EU lawmaker decries Tinder's terrible privacy policy
The dating app Tinder is facing criticism from Europe where lawmakers believe it breaches EU data protection rules. There are calls for the app to be investigated by the European Commission over how it makes use of personal data.
Concerns spring from the fact that Tinder's terms are written in such a way that owner Match Group Inc can continue to use user data even when accounts are closed. It is alleged that these "abusive clauses" are unlawful.

More than 60 percent of Windows users would switch to Mac for more privacy
Concerns over Windows 10 and the amount of data it collects via the Windows Store could prompt users to switch to Mac according to a new survey.
The study conducted by OnePoll on behalf of security and privacy advice and comparison website Comparitech.com finds that 61 percent of the US public who regularly use Windows would at least consider switching to Mac.

Changes are coming to Microsoft's Privacy Statement and Services Agreement
On August 2, coinciding with the launch of Windows 10 Anniversary Update, Microsoft is updating its Privacy Statement. The company is a little light on the details of exactly what the changes are, but says that more will be revealed on the big day. The aim of the changes, as with previous updates is to "eliminate redundancies, improve usability and increase clarity and transparency".
Microsoft makes clear that it is in the habit of sharing user data with others "in certain cases" and it also announces that the Services Agreement will be updated on September 15. You are advised that if you don’t agree with the changes you should "discontinue using the products and services, and close your Microsoft account before these terms become effective".
The SwiftKey keyboard app is busy leaking email addresses and phone numbers to strangers
Who doesn't love a good AI-driven keyboard, eh? Well, people who have discovered that the keyboard is sending their email address and phone number to strangers, for starters. And that seems to be precisely what's happening with SwiftKey.
The Microsoft-owned company has disabled the syncing of data between devices after users complained not only about the appearance of unknown email addresses and phone numbers in suggestions, but also suggestions in unknown foreign languages. The problem became apparent when users who saw the random email address suggestions contacted the owner of the address.

WhatsApp doesn't properly delete 'deleted' chats
A security researcher is warning WhatsApp users that their chats can be retrieved even after they have been deleted, cleared, or archived. Jonathan Zdziarski says that even using the 'Clear All Chats' option leaves behind a 'forensic trace'.
He warns that the only way to be certain that your chat history is deleted, is to get rid of the app entirely. The problem appears to stem from WhatsApp's use of SQLite which fails to overwrite deleted data by default, rendering it recoverable.
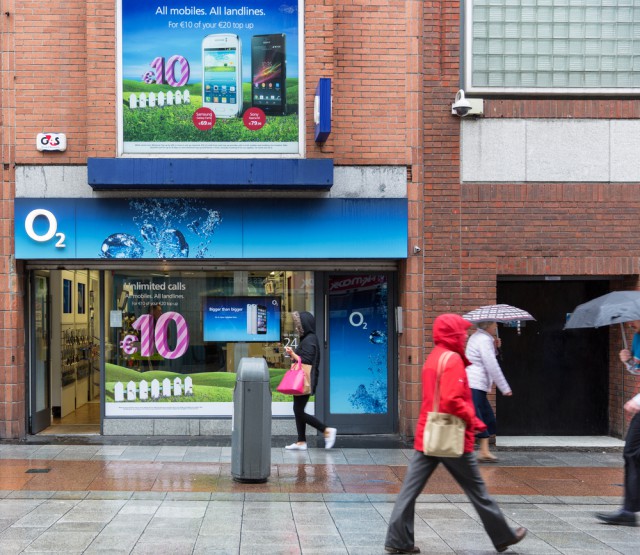

O2 customer information available for sale on the dark web
O2 customer data has been found available for sale on the dark web, most likely as a result of a hack that occurred several years ago.
The gaming website XSplit was hacked three years ago and those responsible for the hack were able to obtain usernames and passwords from the site. Through the process of credential stuffing, in which account credentials acquired through a hack are tested on multiple websites, the hackers were able to gain access and log into O2 accounts.

Every piece of sensitive data could have 1,000 unnecessary copies
Data risk reduction specialist Identity Finder has rebranded itself as Spirion and has released the results of long-term sensitive data audits at three of its largest enterprise sites.
During the audits, the company discovered that if left unchecked, every legitimate piece of sensitive data will create up to 1,000 unnecessary copies.
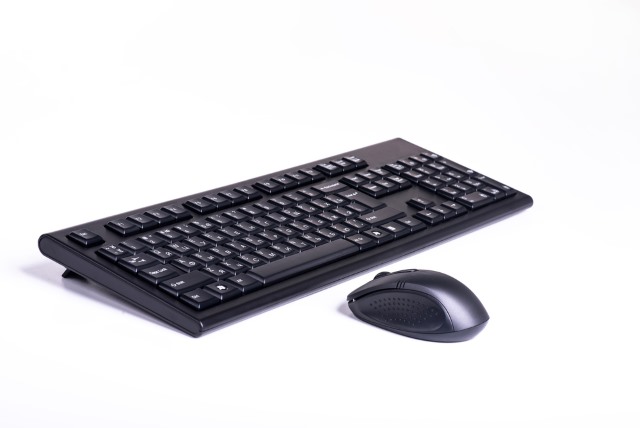

Your wireless keyboard could be secretly leaking unencrypted data to hackers
Researchers at security firm Bastille warn that many wireless keyboards can be very easily intercepted so hackers can see exactly what is being typed. With a very simple dongle called Keysniffer, it is possible to snoop on usernames, passwords and anything else that is being typed from up to 250 feet away.
In all, Bastille found that eight manufacturers produce keyboards -- meaning there are millions in use -- which use unencrypted radio communication to transmit easily captured clear text. The problem affects non-Bluetooth devices from the likes of Anker, Hewlett-Packard, Kensington and Toshiba.

EU-US data-sharing Privacy Shield agreement will run for at least a year without legal challenges
The rocky road to finding a replacement to the Safe Harbour data transfer agreement appears to have become a little smoother. The successor to the EU-US arrangement is Privacy Shield, and European regulators have said it will be permitted to run to at least a year without intervention.
Having been deemed unsuitable because of the level of access it gave the US to European data, Safe Harbor's replacement has been a long time coming. The head nod from regulators will be widely welcomed by the tech industry, as well as those disturbed by NSA surveillance revelations.

Windows 10 telemetry will be used to drive enterprise upgrades with Upgrade Analytics
Rightly or wrongly, telemetry in Windows 10 has been roundly and soundly criticized. But while the feature may be a privacy concern for some, Microsoft says that it is using the data gathered to provide advice to would-be Windows 10 users about driver and application readiness.
This is something that is aimed at enterprise users for whom Microsoft recognizes that certain apps are mission-critical for businesses. This is why the company has launched Upgrade Analytics to "provide customers with insights which allow them to [...] mitigate potential problems".

Judge wants Yahoo to reveal how it recovered deleted emails
Helping out with a drug trafficking case, Yahoo was able to recover emails that had previously been deleted. Now a judge wants to know how this was possible.
Yahoo's only policies state that email cannot be recovered once they have been deleted, and defense lawyers for Russell Knaggs -- who planned to move cocaine from South America -- want to know how the company was able to produce deleted email in this case.

Niantic Labs faces lawsuit in Germany over Pokémon Go privacy concerns
Pokémon Go has proved almost unbelievably popular, and like any app that gains a huge following, malicious versions of the app soon appeared. The game has been in the headlines after hackers knocked gaming servers offline, but there have also been major privacy concerns.
Now there could be a nightmare brewing for developer Niantic Labs in Germany, where consumer advocates say the game violates the country's consumer and privacy laws. Federation of German Consumer Organizations (VZBV) says the company needs to make sweeping changes to a raft of clauses in the app's terms of use in order to avoid further action.

Spotify sells your personal and playlist data to advertisers making you the product
Much like Google, streaming music service Spotify is increasingly turning its attention to advertising. Announcing what it refers to as "programmatic buying", the company reveals that it is launching a targeted advertising program.
Advertisers -- or "buyers" in Spotify's nomenclature -- will be granted access to not only demographic data about users, but also access to information about playlists.

Brexit will not make GDPR mandatory in UK
Another day, another Brexit story. It’s going to be years before we stop hearing the various implications and results of the recently held UK referendum on leaving the European Union.
This time, it’s about private data and its sharing to third-parties, by private companies, without users’ consent.

Microsoft responds to allegations that Windows 10 collects 'excessive personal data'
Yesterday France's National Data Protection Commission (CNIL) slapped a formal order on Microsoft to comply with data protection laws after it found Windows 10 was collecting "excessive data" about users. The company has been given three months to meet the demands or it will face fines.
Microsoft has now responded, saying it is happy to work with the CNIL to work towards an acceptable solution. Interestingly, while not denying the allegations set against it, the company does nothing to defend the amount of data collected by Windows 10, and also fails to address the privacy concerns it raises.
