Google gives in, sets up 'forget me' form following EU ruling

A couple of weeks ago, a European court ruling said that internet users had a "right to be forgotten". Google was at the center of the test case, and the internet giant expressed disappointment at the court's decision that individuals should be able to request that their details be removed from search results. Now a removal request form has been created for those looking to clear their name from search queries.
In order to use the form, individuals are required to provide a "valid form of photo ID". It is then possible to request that information that is "inadequate, irrelevant or no longer relevant, or excessive in relation to the purposes for which they were processed" be removed. Google has already made it clear that it found the court ruling "disappointing", and the company says that submitting a request is no guarantee of having details removed from search results.
NSA: Edward Snowden did not raise surveillance concerns internally

In an interview with NBC earlier in the week, Edward Snowden -- ever a thorn in the side of the NSA -- defended his decision to leak documents to the press, saying "Sometimes to do the right thing, you have to break a law". The whistleblower has long insisted that his revelations were born of a desire to help his country, and claims that he previously tried to voice his concerns about the US government's surveillance tactics through official channels.
Speaking in Wednesday's interview, Snowden said "I actually did go through channels, and that is documented. The NSA has records, they have copies of emails right now to their Office of General Counsel, to their oversight and compliance folks, from me raising concerns about the NSA’s interpretations of its legal authorities". This is something disputed by the NSA who released details of a brief email exchange between Snowden and the Office of General Counsel.
Caught as a hacker? Helping the FBI is your get-out-of-jail-free card

LulzSec is an infamous, famous and notorious name in the technology world. The small collective made a name for itself by attacking high-profile websites such as Fox.com and government sites, but all of this was interrupted when founding member Sabu (or Hector Xavier Monsegur to his mother) was arrested three years ago. Originally facing a jail sentence of more than 26 years for his hacking work, Sabu is now a (relatively) free man having earned himself a get-out-of-jail-free card by working with the FBI since his arrest to help identify other hackers.
Although a judge in New York passed a sentence of seven months, Sabu had already spent this length of time incarcerated so all that is left is one year's supervision. The leniency comes thanks to the fact that Monsegur agreed to continue to work undercover in the hacking community, supplying the FBI with information about activities and individuals. Among those he helped authorities to prosecute were Jeremy Hammond -- one of the most-wanted cybercriminals in the sights of the FBI -- who was jailed for leaking emails to WikiLeaks.
Technology and politics -- two paths that need to cross to enable progress

In the world of politics, the wheels of change move slowly; very slowly indeed. Parties and those in power have a vested interest in maintaining the established order, and any attempts to buck the status quo are usually fairy fiercely opposed. Contrast this with the technological world where there are new innovations made every single day -- even at the weekend! Technology doesn’t run out of money and leave an entire nation on the verge of collapse. Technology is not interested in race, class, sex, sexuality or other characteristics. It is certainly true that technology is largely driven by a desire to generate profit -- we are, for the time being, living in a capitalist world, after all -- but it is profit born of fulfilling people's needs and desires.
Can the same be said of politics? To a large extent politics is self-serving. There's still an interest in generating a profit, but it is for the benefit of the few. Technology serves the masses, and has the potential to serve and benefit all. Of course, the term "technology" is rather broad. For the purposes of this article, I'm going to use it to refer to computers, the internet, smartphone, the cloud, electronic/connected devices, robots and the like. For all the gestures to democracy and choice, politicians are, for the most part, interested in serving certain sections of society. There are of course those parties and politicians who are able to take a wider view, have an interest in helping those at the bottom as much as those at the top, and value all people equally.
The most popular stories on BetaNews this past week: May 18 -- May 24

It should come as no surprise that this week's big news was Microsoft's Surface Pro 3 unveiling. Brian had been looking forward to the NYC event and was at the event to get hands on with the new device. There's certainly a lot to love about Microsoft's third generation tablet, but there is that price to consider. If you like the look of what you see, the device is available for pre-order right now -- and if you're undecided between the Surface and a MacBook Air, Mihaita compared the two. Maybe you're one of those who thinks it’s a niche product.
The Surface Mini failed to make an appearance, but there are still lots of other tablets to choose from -- although they are yet to make much of an impression in higher education, unlike Chromebooks which have found their way into Welsh schools. Will Microsoft's tablet manage to attain the longevity of Apple's iPad? You'd be forgiven for thinking that hell itself had frozen over at the news that work is underway that will make it possible to run Android and iOS apps side by side on the same device.
Facebook listens to feedback and tightens up privacy settings -- a bit
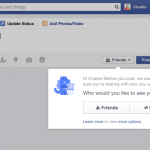
Privacy. It's something that we're all concerned about, particularly online. Facebook is one of many companies that comes in for scrutiny and criticism for the way it handles user privacy, and there have long been complaints about the fact that statuses and uploaded photos are made publicly accessible by default. Today that changes. After years of pestering, Facebook has listened to its user base and changed the default visibility setting to "Friends only". At least this is the case for brand new users.
Anyone signing up for a new Facebook account -- can there be many people left who do not yet have one? -- will be able to avoid accidentally sharing private photos with the world. "Going forward, when new people join Facebook, the default audience of their first post will be set to Friends. Previously, for most people, it was set to Public," says Facebook in a blog post. The first time a post is made, users will be asked whether it should be made public or limited to a smaller audience. If no selection is made, it will default to Friends.
Warning to Android users -- Outlook.com app stores emails unencrypted

Reverse engineering apps is an interesting field of work. On one hand, it can be used by software engineers to determine how an app works so they can copy it. On the other, the method can be used by those with malicious intent to track down weaknesses that can then be exploited. But there's also a third hand. Reverse engineering can also be used to highlight security problems with a view to not only alerting those affected, but also addressing the problem.
Researchers at Include Security, whilst practicing their reverse engineering skills, turned their attention to the Outlook.com app for Android and discovered a potentially worrisome security issue.
PQChat secures your communications using quantum computing-proof encryption
After Edward Snowden’s many (and on-going) revelations, it’s easy to think there’s not much you can really do to avoid being spied upon or prevent your communications potentially being monitored. Of course you probably don’t have much to hide, and therefore what you say isn’t likely to be of major interest to the NSA or other snoopers, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t at least try to maintain a degree of privacy where possible.
SRD Wireless has today announced the launch of PQChat, a free app for iOS based on SRD’s own Never-The-Same (NTS) encryption which protects data using the McEliece cryptosystem, the strongest currently known, and which has never been broken (as far as anyone is aware, at least).
Protect your privacy with Self-Destructing Cookies for Firefox

Self-Destructing Cookies is a Firefox add-on which does a great job of controlling cookie use, without any of the complexity you’ll see in other tools.
Install the add-on and it takes immediate effect, automatically deleting a site’s regular cookies -- and its LocalStorage data -- just as soon as you close its tab.
Google, somehow, gains 100% rating for protecting user data

It may seem as though Google feels the sharp end of many tongues -- be it about problems with Glass, for shaping the content of the internet, or the way it handles advertising. But more often than not, the big G finds itself on the receiving end of criticism for being in bed with the NSA for the way it handles user privacy. In spite of all of the ammunition unleashed in Google's direction, the company has -- incredibly -- been awarded a full six stars out of six by the Electronic Frontier Foundation for protecting user data from government requests.
The EFF's Who Has Your Back? report ranks and rates the performance of some of the biggest names in the world of tech for handling user privacy in the face of government data requests. Finding ourselves in a world now tainted by the activities of the NSA, privacy and accountability have become more important to internet users than ever before. The Electronic Frontier Foundation prides itself on "defending your rights in the digital world", and its annual report looks at the performance and promises of 26 companies who handle your data.
Google preparing an online tool for 'right to be forgotten' removal requests

Google is reportedly readying an online tool which people will be able to use to request that search results pertaining to them are removed from Google's search engine.
This follows a ruling by an EU court earlier this week on the "right to be forgotten", which decided in favor of a Spanish man who had requested that Google remove links (not web content, but search links) which pointed to articles concerning his house repossession for debt repayments. The man claimed that because the incident occurred in the late nineties, it was now "irrelevant", and for it to be made publicly viewable by Google was a violation of his privacy rights.
The most popular stories on BetaNews this past week: May 11 -- May 17

The past week was one dominated by privacy and security related stories. A court ruling in Oracle's favor means that the company is able to claim copyright protection for APIs subsequently used by Google in Android. The long term effects of the ruling are yet to be understood, but they could certainly be far-reaching. Privacy hit the headlines again as SanDisk works on a self-encrypting SSD, and Google was told that users can request that information about them be removed from search results -- of course it didn't take long for the requests to start rolling in.
New research shows that there has been an increase in online suspicion, indicated by a huge increase in the levels of encryption used. The UK government approved the use of Samsung KNOX devices which could help to allay fears about BYOD. Google announced GAME -- Google Apps Message Encryption -- to provide end-to-end encryption for email outside of the Gmail ecosystem.
Google Apps Message Encryption keeps enterprise communication secure

Just yesterday we were looking at how there has been an increase in the level of encrypted traffic online, and today Google announces the launch of Google Apps Message Encryption (GAME). Google is partnering with Zix Corporation to bring fully encrypted communication to enterprise customers even when emailing contacts outside of Google's infrastructure. Emails sent to Google servers have been encrypted by default for a little while now, but the new launch means that emails sent to the likes of Yahoo and Outlook.com will also be encrypted.
As this is a third-party solution provided by Zix Corporation, Google is not offering full customer support for it, but a quick start guide has been published. Available for $35 per user, GAME enables Google Apps customers to not only ensure that the emails they send are encrypted, but also gives the option of setting up custom bounce messages for emails that are sent to unauthorized users who attempt to send encrypted emails.
UK government gives the nod to secure Samsung KNOX devices

Public sector workers in the UK will soon be able to use Samsung handsets after the UK government gave the greenlight to devices running Samsung KNOX. The Communications and Electronics Security Group (CESG) tested the KNOX platform and the government has now published End User Devices (EUD) Security Guidance for Samsung KNOX on certain handsets and tablets. It's not clear whether this paves the way for a new wave of BYOD for government workers, but it is certainly a possibility.
Samsung is pleased with the announcement, and Injong Rhee, Senior Vice President of KNOX Business, IT and Mobile Communications Division, says "Samsung devices with KNOX are already extensively deployed globally across the private sector but now with this significant recognition, government agencies across the UK will be able to adopt Samsung KNOX enabled Galaxy smartphones and tablets setting the scene for other governments to follow".
Is AdBlock Plus killing the web? Massive memory usage is dragging Firefox down

As something of a browser butterfly, I like to keep an eye on what's happening with browsers other than the one I'm currently using fulltime. Like many tech journalists (and non-journalists for that matter), I gave up on Internet Explorer quite some time ago, opting for Firefox initially. I also dabbled with Opera and Waterfox, amongst others, but for a number of years it was Firefox that delivered web pages to me. Sadly, I noticed that things started to slow down. New versions were more bloated and sluggish, and in the search for better performance, I ended up with Chrome. I've been a Chrome user for years now, but I was recently spurred into trying out Firefox once again.
Quite where the impetus came from, I'm not sure -- just one of those "let’s see if anything's changed" moments, I guess. Apart from little quirks like the refresh button being on the "wrong" side of the program window, Firefox seems pretty decent. I was impressed by the sharpness of the display for starters -- I had forgotten that Chrome handles high DPIs very poorly. As I'm using a Surface Pro running at 1920 x 1080, running at 150 percent DPI scaling is essential (I don’t have microscopes for eyes!) and Chrome makes everything look slightly blurry... not enough to put me off -- I'm still using it, after all -- but Firefox was a revelation!
Recent Headlines
Most Commented Stories
© 1998-2025 BetaNews, Inc. All Rights Reserved. About Us - Privacy Policy - Cookie Policy - Sitemap.